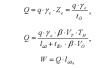How to calculate bonus from salary: formula. How to correctly calculate the quarterly premium in different cases How to calculate the quarterly premium
new entries

Fresh comments

- admin on Transferring a pregnant employee to light work
- admin on Buying goods from an individual: accounting, documents, taxes
- Alexander on Purchase of goods from an individual: accounting, documents, taxes
How to calculate salary bonus correctly?

The bonus system is established in each organization independently. It is defined by Article No. 114 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, where the organization itself determines the frequency of payment of the bonus and its size. Today we will talk about how to calculate the bonus to salary.
First, let's define what a premium is. This is a monetary reward to an employee or his encouragement for excellent work results and good economic performance. The amount of the bonus must be specified in the employment contract, as well as established in the local legal acts of the organization. It can have a fixed amount, or is set as a percentage of earnings.
What do you need to calculate the premium?
— local regulations, for example, a collective agreement;
- order in the form No. T-11 or No. T-11a.
The payment of the bonus is issued by order of the head in a unified form No. T-11 (the bonus is paid to one person) or No. T-11a (the bonus is issued to the team (department, workshop, etc.)).
The percentage of the bonus to earnings, as well as the fixed amount of the bonus, may vary for each employee, therefore it is advisable to issue an order in the form No. T-11 for each individual employee. If the percentage of the bonus or a fixed percentage does not change in relation to the entire team, it is possible to issue a bonus by order No. T-11a.
Case 1. How to correctly calculate the premium for the month?
In the organization, the bonus is set as a percentage of the salary. According to the order of the head, the bonus is paid to all employees of the organization in the same percentage of the salary. How to calculate the premium?
1. We multiply the salary by the bonus percentage.
2. Then we add up the salary and percentage.
Example 1. Ivanov I.I. receives a salary of 10,000 rubles a month. He lives in the Chelyabinsk region, where a regional coefficient of 15% is set. The monthly premium was 10%. Ivanov I.I. received an advance of Rs. Let's calculate the amount of earnings per month, which Ivanov I.I. will get his hands on.
1. We consider the premium.
10,000 * 10% \u003d 1000 rubles.
2. We consider earnings with a premium
3. We consider earnings with a regional coefficient.
11,000 * 1.15 \u003d 12,650 rubles.
4. We consider personal income tax. Let's say he doesn't have children.
12 650 * 13% \u003d 1644.50 rubles
5. We consider the amount for the month that Ivanov will receive in his hands.
Case 2. Calculation of bonuses for employees working at an hourly rate.
1. Multiply the monthly tariff amount by the premium percentage.
2. Then we add up the amount of the tariff and the percentage received.
3. We multiply the amount by the district coefficient - this will be the sum of the accrued bonus and salary.
4. We consider personal income tax. This is the accrued amount multiplied by 13%, or 30% for non-residents.
5. We deduct personal income tax from the accrued amount and deduct the advance payment issued earlier. Get the amount of earnings with a bonus in hand.
The example is the same as in the previous case, only earnings are calculated as the number of hours worked multiplied by the rate per hour.
Case 3. Calculation of bonuses for employees who receive wages from output.
1. The amount of output per month is multiplied by the percentage of the premium.
2. Then we add up the amount of output and the percentage received.
3. We multiply the amount by the district coefficient - this will be the sum of the accrued bonus and salary.
4. We consider personal income tax. This is the accrued amount multiplied by 13%, or 30% for non-residents.
5. We deduct personal income tax from the accrued amount and deduct the advance payment issued earlier. Get the amount of earnings with a bonus in hand.
The example is the same as in the previous case, only earnings are calculated as the amount of output multiplied by the rate of output.
Case 4. Calculation of the premium in a fixed amount of money.
1. We add the amount of the bonus to the amount of wages for the month.
2. We multiply this amount by the district coefficient - this will be the sum of the accrued bonus and salary.
3. We consider personal income tax. This is the accrued amount multiplied by 13%, or 30% for non-residents.
4. We deduct personal income tax from the accrued amount and deduct the advance payment issued earlier. Get the amount of earnings with a bonus in hand.
Example 2. The example is the same as in the first case, only the premium amounted to 1000 rubles per month. (Ivanov I.I. receives a salary of 10,000 rubles a month. He lives in the Chelyabinsk region, where the district coefficient is set at 15%. Ivanov I.I. received an advance payment of 5,000 rubles). Let's calculate the amount of earnings per month, which Ivanov I.I. will get his hands on.
1. We consider earnings with a premium
10,000 + 1,000 = 11,000 rubles.
2. We consider earnings with a regional coefficient.
11,000 * 1.15 \u003d 12,650 rubles.
3. We consider personal income tax. Let's say he doesn't have children.
12 650 * 13% = 1644.50 rubles.
4. We consider the amount for the month that Ivanov will receive in his hands.
12 650 - 1644.50 - 5000 \u003d 6005.50 rubles.
Case 5. How to calculate the quarterly (annual) premium?
A quarterly or annual bonus is paid based on the results of successful performance during these periods.
We add up all the amounts earned (without coefficients) for the quarter (year) and multiply the amount received by the bonus percentage. This is the amount of the premium. The rest of the calculation is in the usual order.
Example 3. Ivanov I.I. receives a salary of 10,000 (January, February, March) rubles per month. He lives in the Chelyabinsk region, where a regional coefficient of 15% is set. We calculate the quarterly bonus, which amounted to 10% of earnings and earnings for April.
1. We consider the amount of earnings for the quarter.
10 000 + 10 000 + 10 000 = 30 000
2. We count the premium
30,000 * 10% = 3,000 rubles.
3. According to the results of the quarter, the bonus is usually issued in the month following the quarter - in April. Then earnings for April will be
(10 000 + 3 000)*1,15 = 14950.
5. Earnings for April to be handed over
14950-1943.5 = 13,006.50 rubles
free book




leave a comment
Accounting services

3 months as a gift

1 module free

free book




In order to get a free book, enter the data in the form below and click the "Get the book" button.
free book




Tired of working? It's time to earn! Download for FREE
free book




In order to get a free book, enter the data in the form below and click the "Get the book" button.
How to correctly calculate employee bonuses

According to the current legislation, the employer has the right to provide financial incentives to his employees for a job well done or for other reasons.
But at the same time, it is necessary to carry out the calculation in an appropriate way, since this payment is income that is subject to personal income tax and must be reflected in accounting accordingly.
The presence of any errors can lead to some problems with the tax authorities.
Basic information

The Labor Code of the Russian Federation expressly states the right of an employee to receive payment for his work.
But in addition to the amount indicated in the employment contract, the employer can pay his employee a different amount, which will also be considered income and act as an incentive.
It is important to remember that it must be properly calculated and reflected in the accounting department.
At the same time, both the employee himself and his employer should definitely deal with some important issues:
Definitions
To exclude a misunderstanding of the legislation in force on the territory of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to know the meaning of the following basic definitions and terms:
Bonus (monetary or in other form) - is a procedure to encourage an employee for the implementation of a certain plan or for a conscientious attitude to their immediate duties.
There are many different types of awards. The procedure for calculating each has all sorts of individual features.
Today, all awards can be divided into the following main categories:
Incentive-type bonuses are usually provided directly by the remuneration system and the format of its payment is mandatory indicated in the employment contract or other regulations.
Incentive bonuses are carried out outside the wage system. But at the same time, it must also be subject to personal income tax, the employer must pay appropriate contributions in favor of various kinds of funds.
A very important point directly related to premiums is personal income tax - personal income tax.
It must be paid by all individuals who are officially employed, as well as being tax residents of the Russian Federation.
The amount of this tax is 13%, it is transferred to the state budget by the employer, who is the tax agent for his employee.
The bonus system must necessarily include the following main elements:
- indicators - grounds for paying bonuses;
- bonus conditions;
- the amount of the premium;
- list of persons to whom the premium is paid;
- frequency of payments;
- grounds for the award.
All these points must be necessarily reflected directly in the intra-organizational regulations.
Whether the premium is included in the calculation of vacation pay, read here.
At the same time, the calculation of the quarterly bonus for the time actually worked must always be carried out in advance.
To whom is issued
A bonus, on the basis of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, can be issued to any employee who falls into a certain category on the basis of signs that are indicated in the legislation or internal acts of the employer.
Today, we can single out the following reasons for making payments to your employees:
- for excellent performance - the company must have documents describing this concept;
- at the end of any amount of work or a year;
- for continuous service.
At the same time, the concepts outlined above are rather vague. It is advisable for the employer to follow some important recommendations:
The amount of the bonus payment can be set as a fixed amount or as a percentage of some important indicator - for example, the income received by the enterprise.
Legal grounds
You should, if possible, study in as much detail as possible the legal basis implying the payment of a bonus. And again, this should be done by both the employee and his employer.
The formula for calculating this payment is as follows:
At the same time, such an indicator as the amount of processed time in days is necessarily taken from the time sheet.
The payment of this particular type of premium is determined as follows:
The main regulatory document that the employer must be guided by when making the calculation is Article No. 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
This payment is subject to mandatory income tax. Income code - 2,000. It is obligatory to make payments to the UST and the FSS.
When implementing accounting, you must be guided by the following:
If possible, you should use a special program 1C. In this way, many mistakes can be avoided.
If quarterly
A quarterly bonus, unlike a similar payment for hours already worked, does not have a clear calculation algorithm.
Therefore, each organization independently draws up a formula for calculating such an incentive.
At the same time, the current legislation contains clear recommendations regarding the establishment of the amount of premiums:
- be sure to take into account the contribution to the result made by each employee;
- the amount of the payment must be justified in economic terms.
I can pay bonuses of this type for the following indicators:
If necessary, the employer can establish a differentiated way of paying bonuses, depending on some important indicator.
It can be the amount of time worked in a particular organization, productivity, or something else.
Usually, the quarterly bonus is accrued to the employee by the employer in the last month of the reporting period (quarter).
One of the most commonly used and simplest ways to calculate this type of bonus is as a percentage of salary.
The act of calculating the premium to the buyer
It is allowed to pay some premium to the buyer by the seller for any specific actions.
At the same time, as a bonus in this situation, the following is usually provided free of charge:
The basis for calculating the amount of the premium to the buyer is a special act. It is an internal document of the organization with which the buyer works and is formed in each case individually by the management of a particular organization.
Example
In order to avoid various kinds of difficulties and problems in the implementation of this type of calculation, it is best to first familiarize yourself with a correctly compiled sample.
Example. The salary of an employee of the company "SM" Ivanov Ivan Ivanovich for a month of work is 30 thousand rubles.
Within the organization, there is a special provision regarding the bonus payment to an employee with a quarterly bonus in the amount of 80% of the salary. For the I quarter, Ivanov I.I. worked 47 working days, while the schedule was 57 days.
In a specific case, the following method was used to calculate the amount of a quarterly bonus for an employee:
At the same time, this amount is subject to mandatory personal income tax in the amount of 13%. Rates in various state funds are charged in the same way as for regular wages.
Whether the district coefficient for the premium is calculated, read here.
Is it possible to reprimand and deprive the award at the same time, see here.
An example of calculating bonuses for employees is common, but payments can be calculated in this way in any organization - if internal regulations allow it and this procedure does not contradict Article No. 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Annual bonus when calculating average earnings in 2017

According to the law, the bonus is part of the salary. That is why it is necessarily used when calculating its average value.
But it is important to remember that this is allowed only in relation to bonuses that are calculated and paid on the basis of the conditions indicated in the letter of Rostrud No. 317-6-1 of February 13, 2007.
According to this provision, the criteria for accounting for the premium on average earnings are as follows:
- this payment is provided for by the wage system;
- funds were accrued for the past year;
- the reason for the payment is labor achievements.
The correct calculation of bonuses to employees is a guarantee of good relations with them and the absence of problems with tax and labor inspectorates.
That is why the employer should study the current legislation well.
The correct wording of employee bonuses: for what can an employee be rewarded? List of grounds for payment

Wage has always been the most controversial topic. After all, if wages are considered a fixed indicator, then the payment of a bonus can only be in cases provided for in the document defining labor relations at a given enterprise. Moreover, the amount of encouragement and the conditions for its receipt are set independently by the employer. Therefore, the bonus procedure itself causes quite a lot of controversy, both among accountants and the employees themselves.
Regulations for issuing an employee bonus

Relations between employers and their employees are regulated by articles in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is the provisions of this document that are the basis for the work of all enterprises in the territory of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, according to the current legislation of the Russian Federation:
- the bonus is paid to employees, if there are grounds prescribed in the document fixing the labor relations between the employer and the employee, that is, a collective or labor contract. Therefore, it cannot be considered a mandatory payment for the work of an employee, as defined in Art. 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- the bonus is considered an integral part of wages, which is indicated in Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- the procedure for calculating bonuses and the conditions for the payment of incentives themselves are prescribed in Art. 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This provision provides for the right of the employer to independently determine both the amount of encouragement and bonus indicators;
- deprivation of an employee of bonuses is considered in Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to the provisions of this article, an employee cannot be deprived of bonuses if the company recorded the fact of a disciplinary violation by this employee;
- issues related to the taxation of bonuses are regulated by the Tax Code, and are established in Art. 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Why do they give an additional payment to the base accruals?

The amount of the bonus, as well as the grounds for its payment, is established by the employer independently, or in agreement with the representative of the labor collective. The enterprise may have established its own reward system, depending on the type of activity, the profitability of the company and even the attitude of the head to the encouragement of his employees.
The actions of employees for which it is best to pay them bonuses, and the reasons for encouraging, not directly related to the success of employees:
- The bonus is given for hours worked. This type of bonus is accrued to employees if they have worked for a whole month without sick days or without days off at their own expense;
- can be rewarded for a job well done. This type of bonus is used not only as an encouragement, but also is a kind of incentive for work in the future;
- bonuses accrued in connection with holidays and solemn dates.
Why might they refuse?

The accrual of bonuses most often depends on the quality of the employee's work, his contribution to the production process, or the professional achievements themselves. Each company sets its own criteria and bonus indicators. But in any case, the employer determines the need to pay a bonus based only on the results of the employee's work.
Based on this, it must be said that it is impossible to reward an employee only for the fact that he has higher education or a particular profession.
Grounds for employee remuneration

The grounds that can be indicated in the provision on bonuses can be indicators:
- for the implementation of the work plan;
- for significant achievements in work;
- for the timely submission of reports;
- for the performance of particularly responsible work;
- for the initiative shown;
- for a job well done;
- for holding certain events;
- for advanced training.
Art. 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for certain liability for delayed payments.
Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Liability of the employer for the delay in payment of wages and other payments due to the employee
If the employer violates the established deadline, respectively, for the payment of wages, vacation pay, dismissal payments and (or) other payments due to the employee, the employer is obliged to pay them with the payment of interest (monetary compensation) in the amount of not less than one hundred and fiftieth of the key rate in force at that time the Central Bank of the Russian Federation from the amounts not paid on time for each day of delay starting from the next day after the established payment deadline up to and including the day of actual settlement.
In case of incomplete payment of wages and (or) other payments due to the employee on time, the amount of interest (monetary compensation) is calculated from the amounts actually not paid on time.
The amount of monetary compensation paid to an employee may be increased by a collective agreement, a local regulation or an employment contract. The obligation to pay the specified monetary compensation arises regardless of the fault of the employer.
When is paper confirmation of the reasons for the promotion required?

Despite the fact that the employer himself determines the conditions and sets the amount of bonuses for his employees, he will need justification for the payment. These include:
- the relevant bonus conditions fixed in the normative act or the collective agreement;
- providing data on the implementation of the plan or the results of the work of a particular employee;
- data that the employee really worked for a full month, did not go on sick leave and did not take time off.
Moreover, I would like to note the fact that justification for the payment of bonuses is necessary only in the case of a one-time bonus. In such cases, the information is recorded in a special document called provision for awards.
But the regular incentives that are paid to employees, carried out without justification.
Incorrect wording in documents

The laws of the Russian Federation do not establish a standard form of a document for the award. But, despite this, there is certain information that must be written in the document. One of the main points of this document is the text itself with the grounds for rewarding an employee.
- Payment according to the tariff for an hour of work. The number of working hours is multiplied by the rate. From the result obtained, the percentage of premium and personal income tax is calculated. In the presence of allowances and coefficients, the amount of the premium is multiplied by the corresponding rates.
- Salary from production. Before calculating the bonus, the amount of output is calculated, and then it is multiplied by the percentage and personal income tax.
- Fixed premium. The amount of additional payment is stipulated in the employment agreement. Its size varies only from regional coefficients.
Receiving a bonus is possible not only as an employee. So, when investing money, a risk premium is calculated. It represents the additional profit arising from the increase in the risk of the transaction. The formula for calculating the risk premium is the product of the value of a stock instrument and the current premium level for it. The premium level is expressed as a fraction.
Found an error? Select it with the mouse and click:
Your finances under control
Reprinting of materials is allowed only with the indication of the original source
Calculation of bonuses to an employee in different situations
Send to mail
Employee bonus payment occurs in the manner established by each employer independently, and may depend on many factors related both to the grounds for accrual and to the algorithms for calculating the bonus. Consider the most common situations of bonus accrual and questions arising from them.
Employee bonuses are calculated as follows: types and sources

The reason for paying an employee such an incentive as a bonus may be:
- achievements of a labor nature, committed both by the labor collective as a whole and personally by a specific employee;
- events that are not directly related to work activities, but caused by the intention to further encourage the employee (for example, in connection with an anniversary or holiday date).
On the grounds of the first group, the employer has the unconditional right to include bonuses in the salary structure (Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), and therefore take them into account as part of the payment for work, i.e., attributing the accrued bonus amounts to the expenses corresponding to the analytics, which will reduce profit base.
It is quite difficult to include bonuses accrued on the grounds of the second group in the salary. The Ministry of Finance of Russia (letter No. 03-03-06/1/14283 dated April 24, 2013) insists on accounting for expenses on them at the expense of net profit.
According to the nature of payments, bonuses can be:
- systematic (regular), the accrual and payment of which is carried out in compliance with the established frequency (once a month, quarter, year or other period of time);
- one-time (irregular), accrued and paid from case to case when an appropriate reason for payment arises.
The bonuses included in the salary structure can have both types of periodicity. But among them, as a rule, systematically paid incentives prevail. Bonuses that are not related to labor achievements are usually one-time.
Despite the existence of different sources for the payment of bonuses, bonuses in any case will amount to the income of the employee. And this income will need to be subject to personal income tax in the usual manner (clause 1 of article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and insurance premiums (clause 1 of article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1 of article 20.1 of the law "On Compulsory Social Insurance against Accidents ..." dated July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ). Moreover, for the purposes of calculating income tax, expenses can include not only those contributions that are accrued on bonuses included in the salary structure, but also related to bonuses not related to labor activity (subclause 49, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 2, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/220).
According to what document is the procedure for awarding

The employer must develop all aspects of the bonus system used by him by himself, setting them in an internal regulatory act (Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This act can be created in the form of a separate document devoted only to bonus issues (provisions on bonuses, incentives, incentive payments). But it is also permissible to include the rules for calculating bonuses as an integral part in the texts of other internal documents on labor law issues:
- wage regulations;
- collective agreement;
- labor agreement.
A specially developed separate document (or part of a document devoted to labor law issues) is convenient for reflecting the bonus procedure used for most members of the labor collective. Its presence allows not to prescribe in detail the rules for calculating bonuses in the labor agreement with each of the employees, but to give in this agreement only a reference to the details of the relevant document on the procedure for bonuses. Thus, the development of a normative act on bonuses makes it possible to enter detailed rules for calculating this incentive in employment contracts only with those persons whose bonuses are carried out on an individual basis.
The Labor Code allows business owners, at their discretion, to approve additional cash payments to employees in order to encourage them for the quality of their work and encourage them to further efforts. Bonuses are paid to employees for a certain period of hours worked - for a month, quarter, half a year and a year. Let's look at how the quarterly bonus is paid - how to calculate it.
Grounds for quarterly bonus payment
Information on the conditions and procedure for paying bonuses should be reflected in the Regulations on bonuses, the Regulations on remuneration, labor and collective agreements.
The quarterly bonus is accrued to employees once every 3 months (quarter). As the basis for its payment, the performance of production work in full is indicated. If the employer wants to encourage employees to overfulfill the norm, he can designate an additional point on bonuses, namely, an increase in bonuses for the fastest completion of tasks.
Typically, the bonus payment is calculated as a percentage of salary, and is not assigned in a fixed amount. Also, its size is related to the profitability of the business - if the company's revenue is small, then bonuses are not paid. And since employers are not required by law to encourage employees with additional payments, administrative penalties cannot be applied to them for non-payment of bonuses.
Cash bonuses are usually set in real production, where it is possible to measure the productivity of employees in terms of output and compare the actual work performed with the planned one. In budgetary organizations, quarterly bonuses are assigned extremely rarely.
The bonus can be accrued to an individual employee who has shown excellent work results, to a group of employees of a separate unit or to the enterprise team as a whole.
Quarterly premium - how to calculate
If the bonus order says that the bonus will be calculated as a percentage of the salary, it will have to be calculated on an individual basis. The premium will be calculated as follows:
- if the employee has worked the entire billing period in full (in this case, 3 months), you need to find the total income, including monthly bonus payments - the result is divided by 3 (months), so the average salary for the quarter is revealed;
- the resulting amount is taken into account when calculating the established percentage for calculating the quarterly bonus;
- the amount received is not issued to the employee until 13% of personal income tax (PIT) is withheld from it.
The provision on bonuses may contain information that the bonus will not be accrued for periods when the employee received the average salary.
The procedure for calculating the quarterly bonus will also depend on the stipulated conditions for its payment in the internal Regulations on bonuses. If the document says that the bonus payment is calculated in proportion to the time actually worked, you will have to exclude from the calculation all the days during which the employee was sick or rested. If such a rule is not provided, the bonus will be paid in full, even if the employee was away from work most of the time.
It happens that the quarterly bonus is assigned in a fixed amount, then it is calculated as follows:
- the amount of the bonus payment is added to the salary;
- the regional multiplying factor is taken into account;
- withholds personal income tax;
- the advance payment is deducted;
- the resulting amount is transferred to the employee.
If the actual hours worked are taken into account when paying the bonus, the bonus payment is assigned differently:
- the amount of output for the considered 3 months is multiplied by the previously approved bonus percentage;
- the result is summed up with wages;
- the multiplying factor is taken into account;
- 13% personal income tax is withheld.
The following formula is used to calculate the bonus for hours actually worked:
PFOV \u003d TS: NRVM x CODE,
where PFOV- bonus for hours actually worked;
TS- tariff rate;
NRVM- standard working time per month;
THE CODE- the number of days worked (from the time sheet).
If the employee works on an hourly basis, the principle of calculating the bonus differs from the above cases:
- the average salary for the quarter must be multiplied by the established bonus percentage;
- the calculated salary is added to the amount, taking into account the increasing coefficients;
- personal income tax is withheld at a rate of 13%;
- As a result, we receive a salary with a quarterly bonus.
Quarterly premium - how to calculate: an example
Employee Karenin Sergey Alekseevich receives a salary in the amount of 67,000 rubles per month. According to the Regulations on bonuses, the company accrues a bonus in the amount of 50% from salary. During the first quarter of the working year, Karenin worked 45 days, and the norm is 56 days.
The amount of the Karenin S.A. will be: (67,000 rubles x 50%) : 56 days x 45 days = 26919 rubles. 64 kop.
The calculation of wages depends on the payment systems adopted at the enterprise, which are enshrined in regulations. In an employment contract concluded between an employer and an employee, the form of work and the payment system must be prescribed, indicating the tariff rate or the established salary for each specific case.
Remuneration: forms and systems
Usually, modern enterprises use the following forms and systems of remuneration: time-based (calculation of wages based on salary, the accrual formula of which will be discussed below) and piecework.
Piecework wages involve remuneration for the actual amount of work (the number of manufactured units of products or services provided) at established rates per unit. Remuneration depends only on the number of units of products or services provided per month, does not depend on the amount of time spent or a fixed salary. Forms of piecework payment:
- piecework premium;
- simple;
- piecework-progressive;
- chord, etc.
The time-based payment system involves payment according to a salary or an established daily or hourly rate. Monthly in this case depends on the actual hours worked per month. She happens:
- simple (fixed payment per month, hour);
- time-bonus (bonuses, allowances, etc. are added to the fixed part).

What is the salary
Remuneration consists of the main and additional parts.
The main part of the salary includes the following types of wages:
- payment according to the salary (tariff), piecework;
- payment and additional payment for work on holidays (weekends);
- for overtime hours;
- premiums;
- allowances for skill, additional payments for harmful working conditions;
- additional payments for substitution and combination of professions, etc.
Additional payments include all additional payments calculated on average earnings:
- payment for all types of holidays;
- compensation payments upon dismissal;
- additional payments up to the average, determined by the regulation on remuneration or other regulatory acts of the enterprise, and so on.
So, labor and its types determine the algorithm for calculating wages for employees of a particular enterprise.
Salary pay: features
The most common and simplest wage is wages. Under this system, the main indicator of successful work is compliance with the working day: working out the planned number of working days (hours) in the billing period (month) guarantees the full salary determined by the employment contract.
Official salary - a fixed amount of remuneration for the performance of official duties in a calendar month. At the same time, it must be understood that the salary is not the amount "in hand" (received after deduction, but the amount to be charged for work in a particular month (before deducting personal income tax and other deductions at the request of the employee).

Salary: how to calculate
To calculate the salary according to the salary (the formula is indicated below), the following indicators are required:
- the established official salary for a fully worked working period (calendar month) - a monthly salary;
- the size of the tariff rate (hourly or daily), which determines a fixed amount of wages for each hour or day worked;
- timesheet showing actual days (hours) worked.
How to calculate payroll correctly? The formula is below:
How to calculate salary for a full-time salary
Employee Ogonkov A.A. Ogonyok LLC in the employment contract stipulates a monthly salary of 45,000 rubles.
He worked all the days according to the production calendar in 2017:
- in May - 20 work. days;
- in June - 21 work. day.
For the worked period, no additional payments provided for by the employment contract, Ogonkov A.A. not supposed to.
For May and June, the employee's salary amounted to 45,000 rubles for each month, despite the different number of days worked.
How to calculate salary for part-time work
Worker Sergeev V.V. the monthly salary is prescribed in the employment contract - 45,000 rubles.
In 2017, in May, he worked ten working days out of the 20 scheduled, on the remaining ten working days V.V. Sergeev was on leave without pay.
Incentives (bonuses, etc.) and other additional accruals (except for salary) to Sergeev V.V. in May 2017 were not appointed.
In this case, Sergeev V.V. (according to the salary calculation formula in the example that is being considered), the following payment is due for work in May 2017:
45,000 rubles (salary for a full working month) / 20 days (planned number of working days in May 2017) x 10 days (actual number of working days in May 2017) = 22,500 rubles.
Often the question arises: "How to correctly calculate the salary for the month?" We suggest using the following table, which shows the formula for calculating wages based on salary when working for an incomplete month.

The formula for calculating wages at the tariff rate
When an employee is set not a monthly salary, but a daily or hourly tariff rate, then the amount of monetary remuneration for the month is calculated as follows:
- at the established daily tariff rate, the calculation of wages is calculated according to the formula:
- at the hourly tariff rate determined by normative acts, remuneration is calculated as follows:
Compensation for work on schedule
The question often arises: "How to correctly calculate wages for those working on a staggered schedule?" or "How to correctly calculate the salary of watchmen according to the schedule?"
At enterprises, often employees of the security service (watchman) work on a staggered schedule, their employment contract provides for a monthly salary.
In this case, payment for the calendar month should be made according to the summarized accounting of working hours.
With this accounting of working hours at the enterprise:
- accounting of planned and actually worked working hours is carried out by the hour;
- a regulatory local act establishes an accounting period (month, quarter, year, etc.);
- the amount of working time in the accounting period should not exceed the established number of working hours;
- the number of working hours in the accounting period is set according to the amount of working time per working week (no more than forty hours a week);
- a normative local act determines the rule for determining the hourly rate at the established salary:
Based on the planned norm of working hours of the calendar month according to the formula:
hourly rate = salary / planned number of working hours of the calendar month for which the salary is calculated.
- monthly salary - 8300 rubles;
- salary is determined for July 2017;
- the planned number of hours in the month of July - 168 hours;
- hourly rate = 8300/168 = 49.40 rubles.
With this calculation, the hourly rate will depend on a particular month and "float" throughout the year.
Or the second method, based on the average monthly number of slaves. hours in a calendar year using the formula:
hour. rate = salary / (norm of working time in hours in the current calendar year / 12 months).
- in 2017 according to the production calendar with an 8-hour work. day and a five-day slave. week work norm. time is 1973 hours per year;
- monthly salary - 8300 rubles;
- hourly rate: 8300 / (1973/12) = 50.48 rubles.
With this calculation, the hourly rate is constant throughout the calendar year.
Payroll when working on a schedule: an example
At the LLC "Ogonyok" enterprise, it was established:
- the established period of summarized working time for accounting is a quarter;
- the tariff rate for watchmen is 50 rubles per hour;
- the shift is 16 hours - daytime, and 8 hours - night;
- surcharge for night time - 20%;
- for the first quarter, the watchman worked 8 days in January, 6 days in February, and 9 days in March.
The payment for one watchman shift is: (50 rubles x 16 hours) + (50 rubles x 8 hours) + (50 rubles x 8 hours x 20%) = 1280 rubles.
The salary is:
- for January - 1280 rubles x 8 days = 10240 rubles;
- for February - 1280 rubles x 6 days = 7680 rubles;
- for March - 1280 rubles x 9 days = 11520 rubles.
Calculation of salary upon dismissal
Often an accountant has a question: "How to calculate the salary upon dismissal?"
On the day of dismissal, according to the Labor Code, the employer pays to the retiring employee all the amounts due to him for wages under the calculation:
- wages for hours worked in the month of dismissal (the day of dismissal is paid as a working day);
- compensation for unscheduled vacation;
- other compensation payments depending on the article of dismissal.

Consider an example of the final settlement upon dismissal.
Lvov S.S. resigns from TES LLC on August 7, 2017 at his own request. On the day of dismissal, the employer is obliged to accrue and pay a salary for work in August, a bonus, a personal allowance, monetary compensation for non-vacation days, that is, to make a final settlement.
According to the employment contract, Lvov S.S. the following fees are set:
- salary for a full working month - 8300 rubles;
- personal allowance - 2000 rubles;
- for work in harmful conditions, the supplement is 4 percent of the salary;
- monthly bonus - 150% for a full working month;
- surcharge for night work - 40% of the hourly rate.
He worked on the total accounting of time, his shift schedule was "a day in three." The hourly rate according to local regulations at TES LLC is calculated based on the average monthly number of hours per year and in 2017 is 8300 / (1973/12) = 50.48 rubles.
S.S. Lviv is entitled to monetary compensation for the days of non-holiday vacation - for 9.34 days.
According to the time sheet in August (on the 7th day inclusive), he worked two full shifts of 22 hours each (44 working hours).
At the final settlement, he was credited with:
- salary payment - 2 shifts x 22 x 50.48 rubles. = 2221.12 rubles;
- bonus for hours worked - 2221.12 rubles x 150% = 3331.68 rubles;
- personal allowance for worked shifts - 2000 rubles / 8 (planned number of shifts per month) x 2 shifts = 500 rubles;
- surcharge for night time - (50.48 rubles x 16) x40% = 323.08 rubles;
- surcharge for harmfulness - 2221.12 x 4% \u003d 88.84 rubles;
- compensation for non-vacation days - 769.53 rubles. x 9.34 \u003d 7187.41 rubles, where 769.53 rubles is the average daily earnings for calculating vacation.
The total salary with all additional charges will be 13,622.13 rubles.
Income tax is supposed to be withheld from this amount (13 percent of the accrued amount): 13622.13 x 13% \u003d 1771 rubles.
Lvov S.S. will receive in his hands minus personal income tax: 11851.13 rubles.
Conclusion
The article considers the formula and an example of its application. The accountant is offered cheat sheets that will allow you to correctly assess the situation and choose the right method of calculation.
Remuneration is a responsible process, we must not forget that the material and moral condition of the employee depends on the income received. Moreover, an incorrect calculation may result in sanctions from the labor inspectorate and tax authorities.
So, the calculation of employee remuneration is based on:
- an employment contract between an employer and an employee;
- an admission order indicating the day the employer began working;
- production time sheet;
- local regulations (orders on encouragement or regulation on remuneration and others);
- production orders, acts of work performed, etc.
Each accrual for the payment of monetary remuneration for work must be accompanied by a document and a normative act.
In case of overfulfillment of planned indicators, an increase in the size of the envisaged bonus is possible. It is advisable to indicate information regarding this opportunity in the employment agreement. If the enterprise fails to achieve the planned targets, then all of its employees or exclusively representatives of a particular department who are responsible for this state of affairs may be deprived of the bonus. In most cases, employers tie bonuses precisely to planned standards, since the profitability of the enterprise depends on this. Naturally, with low profitability or its complete absence, it becomes inappropriate to pay bonuses.
How to calculate salary bonus
Attention
A regulatory legal act of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation may establish a limit on the increase in the district coefficient established by municipalities that are part of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation. The amounts of these expenses are related to the cost of wages in full.
The essence of this coefficient is that it is the delta of the increase in monthly earnings for work in difficult climatic conditions. This multiplier is calculated on the monthly payments established by a particular employer, in accordance with the provisions of the employment contract, and therefore on incentives.
Important
We also take into account that the quarterly promotion is usually issued in the calendar month following the quarter, along with the monthly rate. At the same time, the specified coefficient is calculated both for wages and for incentives.
How to calculate an employee's salary bonus?
Info
For example, if the document stipulates that an employee is entitled to a quarterly bonus, but the conditions for receiving it are not taken into account, then the entrepreneur will have to pay it regardless of the performance. Otherwise, employees have the right to file a complaint with the regulatory authorities.
How to correctly calculate the quarterly bonus It is important for the head of the enterprise and his accountant to understand how to calculate the quarterly bonus. In general, this is done by adding up all the income received for the reporting period and multiplying the amount received by the stipulated premium percentage.
Calculation example: Salary of Rashidov D.I. for each month of the second quarter (April, May, June) amounted to 31 thousand rubles. He lives in the Chelyabinsk region, where a district coefficient of 15 percent was set.
Prednalog.ru
However, this issue is not the subject of this article. An employee of the company's personnel service often acts as an assistant accountant in matters of calculating incentive payments.
He, as a rule, is better acquainted with the primary sources that contain the procedure and methods for calculating incentive payments (which include the relevant internal regulation, as well as the collective agreement). What is the maximum and minimum score? Article 144 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is devoted to the issue of the magnitude of incentive payments to workers.
At the same time, if the previous version of this article did not provide for restrictions on the amount of bonus payments and left this issue at the mercy of the employer, then in this version such a democratic approach applies only to non-state structures.
How to calculate salary bonus: formula
For information on what points should be reflected in the regulation on bonuses in relation to quarterly bonuses, read the article "Calculation of the quarterly bonus for the time actually worked." What coefficients are used when calculating the bonus The rules for calculating bonuses may not make the procedure for calculating it dependent on any other conditions, except for the amount of salary and the size of the share established for calculating bonuses.
In this case, the premium actually becomes fixed. Its size will not depend on the time of actual work or the rules for depriving the bonus. The amount of bonuses in such a situation can change only if the accrual base, i.e. salary, changes.
Payroll, online calculator
In most cases, the bonus is not fixed, although such an option is allowed by law, but depends on the salary of each individual employee. Who is not entitled to remuneration The Labor Code distinguishes two categories of persons who are not entitled to the accrual of monetary remuneration: the first - women who have been on parental leave throughout the quarter (in case of partial occupation of the quarter, a recalculation is provided); the second - persons who were fined, reprimanded or received other disciplinary sanctions in the current quarter.
It is important for the employer to draw up employment contracts correctly and clearly spell out the conditions for possible bonuses in them.
Premium calculation
It is considered separately, as the ratio of days of absence and presence at work in the quarter. In a similar way, an additional payment for the year is considered. Salaries paid for 12 months are taken into account.
The law establishes a list of persons to whom additional remuneration is not charged. These include:
- employees on maternity leave;
- employees who are subject to disciplinary action;
- workers temporarily suspended from duty.
Coefficients in the calculation If only the amount of salary and a percentage of it are used to calculate additional remuneration, then the additional payment is practically fixed.
Its size does not change from the number of working days in a month, the fulfillment of plans, etc. The change in the salary itself affects the amount of the payment.
How to correctly calculate the quarterly premium in different cases
We consider what Vaskin will receive a monthly salary and incentive payment, taking into account the regional coefficient of 15%: (25,000 + 6,679.68) x 1.15 = 36,431.63 rubles. It should be noted that the above formulas are fundamental and may vary depending on specific actual circumstances. In conclusion, I would like to say that the question of the correctness and fairness of the procedure for calculating incentives for the fighters entrusted to you as the head of the company is entirely in your hands. Settle this issue with the company's internal documents, and this will help you properly stimulate the team and encourage it to perform labor exploits, which will become a good prerequisite for business development.
Accrual data were carried out for 12 months in a row. It is necessary to calculate the annual premium, the amount of which is 15%:
- total salary for 12 consecutive months:
- Calculate the annual premium:
- the amount of personal income tax deducted from the annual premium:
Ultimately, at the end of the year, the employee will receive a bonus in the amount of 18 thousand rubles.
rubles - 2,340 rubles = 15,660 rubles.
Direct accruals to special insurance funds should be carried out at the expense of the employer himself. It is important to remember: there is a certain list of persons who do not receive quarterly and annual bonuses.
It is reflected in the current legislation on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Calculation of payments under different payment conditions Depending on the conditions and sphere of work, wages have their own characteristics of calculation. A fixed salary is not set at every enterprise.
As a result, the calculation of the premium is carried out in different ways:
- Payment according to the tariff for an hour of work. The number of working hours is multiplied by the rate. From the result obtained, the percentage of premium and personal income tax is calculated.
In the presence of allowances and coefficients, the amount of the premium is multiplied by the corresponding rates.
- Salary from production. Before calculating the bonus, the amount of output is calculated, and then it is multiplied by the percentage and personal income tax.
- Fixed premium.
The amount of additional payment is stipulated in the employment agreement. Its size varies only from regional coefficients.
Receiving a bonus is possible not only as an employee.
salary bonus calculator
We multiply the amount by the district coefficient - this will be the sum of the accrued bonus and salary.4. We consider income tax. This is the accrued amount multiplied by 13%, or 30% for non-residents.5. We deduct personal income tax from the accrued amount and deduct the advance payment issued earlier. Get the amount of earnings with a bonus in hand. Example 1
Ivanov I.I. receives a salary of 10,000 rubles a month. He lives in the Chelyabinsk region, where a regional coefficient of 15% is set. The monthly premium was 10%. Ivanov I.I. received an advance of Rs.
Let's calculate the amount of earnings per month, which Ivanov I.I. will get his hands on. 1. We consider the premium. 10,000 * 10% \u003d 1000 rubles. 2. We consider earnings with a premium of 10,000 + 1,000 = 11,000 rubles.
We consider earnings with a regional coefficient. 11,000 * 1.15 \u003d 12,650 rubles. 4. We consider personal income tax. Let's say he has no children. 12 650 * 13% \u003d 1644.50 rubles 5.
From the final result, 13% personal income tax is calculated or 30% for non-residents of the Russian Federation. The employer pays contributions to the Pension Fund.
An example of calculating employee bonuses:- 25000 (salary) * 30% (bonus percentage) = 7500;
- 7500 * 13% = 975;
- 7500 – 975 = 6525.
The presented example is the simplest calculation of remuneration.
The enterprise may apply additional indicators reflected in internal documents:
- purpose of the award;
- accounting of hours worked;
- payment periods;
- conditions for deprivation of remuneration as a result of detected violations;
- the procedure for calculating bonuses during periods of change in salary.
How the Quarterly Bonus is Calculated The Quarterly Bonus is paid based on successful performance over a three-month period.
Bonus payments by employers to employees at the end of the year is a form of incentives. The normative act of the enterprise is the Regulation on bonuses, developed by the commission or the head and presented to the team for review. The document is a local act, which allows you to include positions that best reflect the specifics of the enterprise. The annual bonus is calculated on conditions that should not contradict the current civil and labor legislation.
Annual bonus accrual
Labor legislation defines bonus payments as incentive payments, which are part of the employee's salary (Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The peculiarity of the award is the need to determine the indicators that give the right to an incentive payment. The Regulation establishes the basic conditions for the calculation of bonuses.
| Article | Description |
| Indicators that allow employees to qualify for the annual bonus | Depends on the type of activity and form of remuneration |
| Bonus Funding Sources | Ordinary business expenses or profit after tax |
| Persons eligible for the award | The right should be granted to all full-time employees. Different types of bonuses can be applied for groups of positions. |
| Number of months worked to receive bonus | Full year or pro rata hours worked |
| Terms of payment and the possibility of transferring payment | Terms are determined depending on the organization of work and the structure of the enterprise. For example, subsidiaries receive bonuses after the head offices approve internal reports. |
| Restrictions on the size of the payout fund in the absence of sufficient funds | Refusal to pay bonuses is based on unprofitable activity. The probable option of reducing the amount or refusing to pay must be specified in an internal document |
| Benefit forfeiture rates | Determined at the discretion of management |
| Special cases | The cases of payments upon termination of the contract are considered, the dependence of payments on the article of dismissal |
To fulfill the conditions of bonuses, check the compliance of persons with the requirements and make the calculation, the enterprise appoints a responsible person or commission. Practice shows that the final decision on the appointment of the annual bonus is the prerogative of the head.
An example of a common mistake when determining the circle of bonuses
The Aktiv enterprise submitted for the approval of the team the Regulations on bonuses developed by the commission. The document identified persons who are not entitled to receive bonuses - employees registered under GPC agreements, seasonal workers employed for the summer period, external part-time workers.
Representatives of the labor collective did not approve the Regulation, citing discrimination of the rights of part-time workers (Article 132 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Persons accepted under an employment contract as part-time workers have rights and guarantees similar to the rights of persons with contracts for the main employment. The regulation on bonuses for the Aktiv company has been sent for revision.
Indicators for the appointment of annual bonuses
When determining performance indicators, different working conditions are considered to receive incentive payments. The local act provides for distinctive conditions for different professions and positions of employees, forms of remuneration. Read also the article: → "". Approximate bonus rates for common forms of remuneration:
| Form of remuneration | Award indicators | Premium Reduction Indicators |
| piecework form | Achievement of monthly or quarterly revenue plan, saving material resources | Non-fulfillment of the plan, violation of labor discipline |
| time-based form | Implementation of advanced working methods, mastering technology, participation in company projects, implementation of the board by the production structure | Complaints for violating the routine and making mistakes, reducing production indicators in the whole department |
| Piecework premium | Improvement of qualitative and quantitative production indicators | Reducing the variable component of remuneration, violation of labor protection rules |
The document regulating the payment of bonuses must define the conditions for depriving the promotion. The basis for the complete deprivation of the bonus is a serious misconduct of the employee - absenteeism, replaced by a disciplinary sanction, appearing at work in a state of intoxication, deliberate damage to property.
The use of flexible performance indicators for calculating the amount of bonuses does not exclude the possibility for the employer to determine a fixed part. The purpose of the award can have 2 components - a fixed and a variable part.
Types of bonuses
The amount of bonus remuneration is determined depending on the procedure specified in the Regulation on bonuses. The company can set up various accrual options:
- Payment of average earnings in proportion to the time worked during the year.
- Payment taking into account the coefficient depending on the length of service at the enterprise.
- The amount calculated according to the coefficient of labor participation (KTU) when bonuses are paid to the teams of workshops, team contracts.
- Payment without additional conditions in the amount of salary or a fixed percentage of the amount, subject to the indicators of the purpose of the bonus.
The choice of the type of bonus is determined by the employer based on the specifics of the activity and based on the reasonableness of incentives.
Calculation of the premium amount using the formula
The most common payment option is a fixed amount based on salary, calculated in proportion to hours worked. To obtain the amount, the calculation formula is used: Pr \u003d Pr norms / Dn norms * Dn work, where:
- Pr - the amount of the premium to be paid;
- Pr norms - the size of the maximum available premium;
- Days of norms - the number of standard working days in a year;
- Days worked - the number of days actually worked.
In addition to the popular simple method of calculating bonuses for workers on a time-based form of remuneration, there are less popular options.
An example of calculating the premium using KTU
The Compass organization set up an annual bonus fund to reward installers K., M. and P, who work in a team way. The total amount of the award was 30,000 rubles.
According to the terms of the employment contract and the Regulations on bonuses, the distribution is made by the foreman according to the amount of useful participation. As an indicator of KTU, the foreman takes the man-hours spent by each employee. As a result, K. received 40% of the amount, M. - 35% and P. - 25%.
Order and statement for the payment of bonuses
The basis for the payment of bonuses to employees is the order. In personnel workflow, the form of order No. T-11 is used to reward one employee or No. T-11a when encouraging a group of people. Read also the article: → "". Documents from the album of unified forms have not been mandatory since 2013, but continue to be used as the most optimal forms for primary accounting. The employee must familiarize himself with the data of the order against signature.
The bonus is issued according to a separate statement or as part of monthly payments, depending on the source of payments and the expense write-off account.
In accounting, statements are used:
- Settlement and payment form T-49. Used to place data on the accrual and issue of amounts. It is the most optimal form for paying bonuses in cash.
- Settlement form T-51. It is used when transferring bonuses to the employee's salary card.
- Payment form T-53. It is used when issuing a cash premium in the inter-settlement period, upon payment of which personal income tax is charged in the total amount of accruals.
Terms of payment of premiums
The terms for payment of wages and its parts (bonuses) are established by the new edition of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The amended article, which entered into force on September 3, 2016, determines the period for paying employee benefits within 15 days after accrual. Employers have the right to set any date for the calculation of bonuses:
- The last working or calendar day of the year at the same time as payroll.
- The date set after the adoption of internal reporting by the founders.
- The day following the submission of the annual accounts.
In the explanations of the Ministry of Labor to the new edition of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, posted on the official website of the Ministry, it is noted that employers can independently determine the period of payments with the fixing of the order in the collective agreement, Regulation on bonuses or order. Labor legislation will not be violated if the provision on setting the deadline for calculating bonuses by order is fixed in local acts.
After accrual of the premium on the due date, payment is made within 15 days. An employer who has violated the deadline for payments to employees after accrual is subject to an administrative fine.
An example of the timing of bonus payments:
The Progress enterprise has set the date for accruing the bonus for the year - March 15, 2015. An appropriate order was issued on the appointment of bonuses to employees. The payment of the premium by the Progress enterprise must be made no later than March 30. Exceeding the deadline will be considered as a violation of labor laws.
Sources of bonuses at the enterprise
The enterprise in the Regulation on bonuses must fix the sources of financing, the type of which determines the accounting of the operation and taxation. One of the financing options is provided:
- From profit after tax.
- At the expense of expenses from ordinary activities.
Depending on the source of funding, transaction postings are determined:
The sums of bonuses are accrued contributions to the insurance funds. In the month of payment, the employee withholds personal income tax with simultaneous transfer to the budget.
Additional reflection of the premium
Annual bonuses received are not reflected in the employee's documents. The employee must be aware of the possibility of receiving bonuses at the end of the year, which is confirmed by the signature in the order.
An example of erroneous reflection in documents of information about bonuses:
Enterprise "Akkord" determined the possibility of bonuses for employees at the end of the year. In the order issued at the enterprise, a personnel worker made a clause about recording bonuses in the work book. During the inspection, the Labor Inspectorate made a remark, pointing out a violation of Art. 66 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Indicators of personal achievements are entered into the work book. Bonuses, the right to which is established in a collective agreement or other act, should not be reflected in the work book.
Question number 1. Is it possible to claim a bonus for a dismissed employee if the person has fully worked the calendar year without complaints, but at the time of dismissal, the bonus order was not issued?
The payment of bonuses at the end of the year and the list of persons is determined by the employer independently and voluntarily. In the absence of payments, violations of labor legislation are not made. If the Regulations on Bonuses stipulate a clause on the payment of bonuses only to full-time employees at the time of issuing the order, there is no opportunity to challenge the loss of funds.
Question number 2. Can the manager determine the circle of bonuses, regardless of performance indicators.
No, the actions must be justified. The Regulations on bonuses should set the parameters for assigning bonuses. The head is the same employee as the rest of the employees and must adhere to the rules established by the company's documents.
Question number 3. Is it possible to transfer bonuses to a salary card?
You can, bonus payments are part of the salary.
Question number 4. Are bonus amounts included in the amount of income taken into account when calculating vacation pay?
Bonus amounts are included in the composition of income taken into account when determining the average wage.
Question number 5. Are there limits on the maximum amount of bonuses?
The legislation does not limit the upper limit of payments. The amounts are determined by the employer.