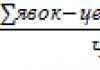What does normalized and non-standardized schedule mean. Irregular working hours: practical application issues
Irregular working hours - a special mode of work, in accordance with which individual employees may, by order of the employer, if necessary, be occasionally involved in the performance of their duties. labor functions outside of their working hours. The list of positions of employees with irregular working hours is established by a collective agreement, agreements or local normative act adopted taking into account the opinion of the representative body of workers.
For an employee working on a part-time basis, an irregular working day can be established only if, by agreement of the parties to the employment contract, a part-time working week is established, but with a full working day (shift).
Comments to Art. 101 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. The commented article reveals the concept of "non-standardized working day" and indicates that the list of positions of employees with such a working day is established by a collective agreement, agreements or local regulatory act adopted taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees. For the first time at the legislative level, the article reveals the main features of this type of working day: work by order of the employer outside the normal working hours.
2. An irregular working day, as indicated in the commented article, is established for certain categories of workers with special conditions labor, when, due to production needs, on certain days of the week they are allowed to perform work in excess of the normal working day, as a rule, without additional payment or compensation in the form of time off. Therefore, an irregular working day is introduced for certain categories of workers who usually occupy leadership positions in the organization, and for specialists whose work cannot be accounted for in time. For example, on November 1, 2007, the Board of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation adopted Decree N 274p "On approval of the List of positions for employees of the PFR system with irregular working hours and the establishment of the duration of the annual additional paid leave for employees of the PFR system."
However, these workers are subject to general rules regarding the start and end time of work. Their processing is not considered overtime work and is therefore not subject to increased pay. Compensation for processing on certain days of the week in excess of the established working hours is provided in the form of additional paid leave. The procedure for granting such leave is determined in local regulations or in employment contract when hiring, since irregular working hours are one of the working conditions for these workers (Article 119 of the Labor Code).
The establishment of an irregular working day does not mean that these workers are not subject to the basic provisions of labor legislation on the norms of working hours and rest time. Therefore, involvement in work outside the normal working hours cannot be systematic.
3. When an employee is involved in work outside the normal working day, his consent is not required, since this issue is negotiated when concluding an employment contract.
Some regulations establish that irregular working hours are introduced for certain categories of workers, for example, for drivers cars, except for taxi drivers (Regulations on the peculiarities of the working hours and rest time of car drivers approved by Order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated August 20, 2004 N 15).
4. In a letter Federal Service on labor and employment of June 7, 2008 N 1316-6-1 "On work in the irregular working day" states that in accordance with Art. 101 of the Labor Code, an irregular working day is a special mode of work, in accordance with which individual employees may, by order of the employer, if necessary, be occasionally involved in the performance of their labor functions outside the working hours established for them.
An employee may be involved in the performance of his labor functions both before the start of the working day (shift) and after the end of the working day (shift).
From Art. 119 tk in new edition the rule was excluded that if the employer does not provide additional leave for the use of an employee in irregular working hours, processing in excess of the normal working hours from written consent employee is compensated as overtime.
Thus, the Labor Code does not recognize overtime work during irregular working hours, in which certain guarantees must be observed (for example, limiting hours of processing, additional pay), and Art. 97 of the Labor Code, which provides for the possibility of processing in two cases (for overtime work and for work in irregular working hours), in fact, confirms this. In other words, for work in the irregular working hours, compensation is provided only in the form of additional leave, the duration of which is determined by the collective agreement or the rules of the internal work schedule and cannot be less than 3 calendar days.
At the same time, the introduction of an irregular working day for employees does not mean that they are not subject to the rules that determine the start and end time of work, the procedure for recording working time, etc. These workers are on a general basis released from work on weekly rest days and holidays.
Thus, the involvement of employees who have an irregular working day to work on their weekends and non-working holidays should be carried out using the provisions of Art. Art. 113 and 153 of the Labor Code.
It should also be borne in mind that the involvement of employees to work outside the working hours established for them should not be systematic, but should occur from time to time (sporadically) and in certain cases.
The irregular working day is considered in the legislation as an alternative to the 8-hour working day. Management is free to decide whether it is enough for employees to be on site for the usual number of hours to complete all work, or they need additional time for certain tasks. If the need for this nevertheless arises, an irregular day is introduced for specific employees locally.
How the irregular working day is interpreted in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
In the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which is designed to regulate relations between management and subordinates, a lot of attention is paid to establishing norms of time spent at work that are not harmful to health, as well as norms of time that the body will have enough to recuperate, including an irregular working day.
What period the employee must stay within the company, performing his labor functions, is specified in the "Working hours" section. Within the framework of this concept, as well as the concept of "non-standard working day", it is fixed how many hours an employee must perform his duties throughout the day (in some cases, the term "shift" is used instead of a working day). There are also time limits for the workweek and year. Separately, there is the concept of "rest time". With its help, the duration of daily rest, weekends and holidays is regulated.
Standard working time perceived as a 5-day week with an 8-hour work day. It is this rule that operates in the vast majority of enterprises and organizations, both public and private. But there is another mode of operation - an irregular working day (Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Irregular working hours are not introduced for the entire enterprise, but only for some individuals who simply need to work above the plan. It turns out that the whole company has, for example, a standard 5-day workday with a start at 9 am, and individuals work irregular hours. Their duties include showing up for work at, say, 6 a.m. or leaving the office after 10 p.m.
For many, irregular working hours are tightly intertwined with the concepts of "overtime" and "processing". But at the legislative level they are separated. An irregular working day is a separate mode of work that allows the employer to use specific workers outside of their regular schedule.
How many hours per week and year is it permissible to work in 2019
In Russia, a working week of 40 hours is considered the norm (Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If a we are talking about a 5-day week, and this is how they work at the vast majority of enterprises, then the employee has to work 8 hours daily. But the employer has the right to increase these norms.
This increase is of 2 types:
Don't know your rights?
- attraction to overtime;
- stretching the schedule as part of an irregular working day.
The law introduced a restrictive framework for overtime work: it is impossible for such processing to exceed 120 hours per year. At the same time, it is prohibited to involve an employee in overtime work lasting more than 4 hours 2 consecutive days.
But in relation to the irregular working day, there are no clear time limits in the law. There are only requirements that are not expressed in a specific hourly equivalent. The regime of an irregular working day should be episodic, that is, there can be no talk of any system. In addition, the employer needs to really need the employee to perform his direct duties during irregular working hours.
Irregular working hours - what does it mean for an employee
An employee who has agreed to an irregular working day needs to know the following:
- The employer will not each time ask the consent of the employee to work an irregular working day. Such consent is obtained once and is most often reflected in the employment contract.
- Refusal to work an irregular working day can be equated to a refusal to fulfill one's labor duties. Although the courts have not yet developed a unified practice of resolving labor conflicts on this issue. At the same time, you need to understand that every day such a schedule is unacceptable. Irregular working hours are an episodic occurrence in daily activities.
- Let this mode working hours and is called an irregular working day, this does not mean that there should be no restrictions on its duration. The local act and the employment contract should describe the time frame of the working day and week. Irregularity lies in the difference between the schedule and the generally accepted in the company.
- A person who is called upon to work an irregular working day must understand that this is impossible on permanent basis. The employee is obliged to come and go with the rest of the employees, and only if such a need arises to work overtime.
- An irregular working day cannot serve as a reason for the performance of additional duties not prescribed in job description. Increased work time, not the list of duties.
An irregular working day gives the employee a bonus in the form of at least 3 vacation days, which are paid by the company. These days can be attached to annual leave. Also, instead of a vacation, you can get monetary compensation. The same rules apply here as for annual paid leave. It’s just that there may not be additional payments for irregular working hours if the authorities do not order this.
What does irregular working hours mean for an employer?
A boss who has a need to establish an irregular working day for his employees must first arrange everything. To begin with, it is necessary to reflect the very possibility of attracting persons to work within the framework of an irregular working day in an agreement between the team. It also needs to specify a list of positions for which an irregular working day is required.
Then you need to conclude with each employee who holds a position from this list, an agreement on the introduction of irregular working hours, and in writing. Oral agreements do not apply in this case. The easiest way is to initially prescribe this in the employment contract, and if it has already been agreed, you will have to correct it by introducing a clause on irregular working hours.
The employer must understand that he does not have the right to force an employee to work an irregular working day every day or even every other day, since this mode is strictly episodic. At the same time, during the time worked out by an employee in excess of the norm, one cannot force him to take on additional functions. Non-normative working hours are used only for the performance of the direct duties of the employee.
The list of positions of employees with irregular working hours
The circle of persons who can work irregular working hours is established almost arbitrarily at the local level. There is no single list of positions with irregular working hours in the legislation. You can find only a few recommendations on this issue.
So, in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation "On approval of the rules for granting additional annual leave to employees with irregular working hours" dated 11.12.2002 No. 884, it is proposed to include the following positions in the list:
- Leading link. For example, a CEO can easily work irregular hours.
- Maintenance personnel. The same adjuster can come to work in advance during irregular working hours to check the equipment.
- Housekeeping staff. The departure of the caretaker to work off an irregular working day can simplify the work of all staff.
- Employees whose time spent at work is not accountable. The realtor can organize property showings during irregular working hours.
- Employees with an obligation to work certain time, but the period when this must be done is not specified. These may include persons creative professions for whom an irregular working day is quite the norm.
So employers can see some freedom in choosing positions with irregular working hours. In private structures, irregular working hours are established almost entirely at the request of the authorities. The main thing is that the list of positions should be fixed in writing.
The rules for regulating such a regime as an irregular working day, in labor law expressed indistinctly. The very norms that regulate irregular working hours as a mode of work are scattered throughout the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and not collected in a separate subsection. In this regard, when establishing and applying irregular working hours, special care must be taken to prevent violations of the law and not to confuse irregular working hours with overtime and overtime work.
At the same time, as representatives of Rostrud recently pointed out, this does not mean at all that these employees should be at the disposal of the company around the clock without any compensation.
According to the Labor Code, an irregular working day is a special mode of work, according to which individual employees may, by order of the employer, be occasionally involved in the labor process outside the working hours established for them (Article 101 of the Labor Code). At the same time, the legislation does not contain any, even a standard, list of positions for which this work schedule can be established. Article 101 of the Code leaves the compilation of such a list at the discretion of the organization, although the opinion of the trade union must be taken into account without fail.
Thus, the list of categories of workers with irregular working hours can be approved by a collective agreement, agreements or local regulations. Since the working hours of such employees will differ from general rules operating with this employer, then the condition of irregular working hours, in addition to everything else, must be reflected in the employment contracts concluded with them. As compensation for such working conditions, the employer is obliged to provide such specialists with annual additional paid leave, the duration of which must be at least three calendar days (Article 119 of the Labor Code). But at the discretion of the company, additional “rest” for employees with irregular working hours can last longer. As employees of the Federal Labor and Employment Service explained in letter No. 1316-6-1 dated June 7, 2008, no other payment for work in excess of the established working hours is required in this case.
No overtime
In their epistolary creation, representatives of Rostrud emphasized that for work in the irregular working hours, compensation is provided only in the form of additional leave. If earlier, they pointed out, Article 119 Labor Code ordered the employer to pay for processing as overtime in the event that “irregular” employees do not provide “extra” days of rest, the current version of this norm does not put forward such requirements. In other words, officials explained, the Code does not recognize overtime work during irregular working hours. This means that there is no need to comply with certain guarantees, such as limited processing hours and additional fees.
At the same time, specialists from the Federal Labor and Employment Service recalled that an irregular working day for an employee does not mean that the rules determining the start and end time of work, the procedure for recording working time, etc., do not apply to him. Such an employee, of course, can be involved in the performance of his labor functions both before the start of the working day or shift, and after they end, but not on weekends or holidays. In this case, representatives of Rostrud noted, there are already general rules, that is, articles 113 and 153 of the Labor Code. In other words, even if an irregular working day is set for an employee, his work on a weekend or holiday must be paid double, or, at the request of the employee, he can be provided. True, the non-working day worked in this situation will still have to be paid, but already in single size.
In addition, experts from the Federal Service for Labor and Employment warned employers against abusing the opportunities provided to them by the irregular work schedule of the staff. Involving workers to work outside the established working hours for them should not be systematic, but occur from time to time (sporadically) and in certain cases, they pointed out.
Taxation of additional holidays
As already mentioned, the employer company has the right to decide for itself how many days to add to the vacation of "irregular" employees, the main thing is that the additional rest lasts at least three calendar days. But the company is obliged to pay the employee all the days of additional leave in the same manner as the main one. So, in order to take into account such costs when calculating income tax, it is first of all necessary that the “extra” days of rest be provided in accordance with all the rules. In other words, the organization must necessarily have an approved list of positions with irregular working hours, the condition for such "processing" must be fixed in the employee's employment contract. In addition, the collective agreement or internal regulations must establish a specific duration of vacation-compensation, which again must be reflected in the provisions of the employment contract. If all these requirements are met, additional ones can be included in labor costs based on the Tax Code. Moreover, they can be taken into account in full, and not just for the three days laid down by the "non-standardized employee" directly by law. As representatives of the main financial department explained in a letter dated January 9, 2007 No. 03-03-06 / 4/6, provided that the procedure for providing additional rest for an irregular working day is determined by the employment contract, payment for such a vacation is recognized as an expense in actual amounts. But in this case, the company will have to accrue UST for the amount of vacation pay in excess of the three days established by the Labor Code. The financiers came to this conclusion in a letter dated February 6, 2007 No. 03-03-06/2/17, citing paragraph 3 of Article 236 of the Tax Code as an argument. Apparently, the experts of the Ministry of Finance are not inclined to qualify “excessive” leave as legally established compensation, which, on the basis of subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 238 of the Code, would exempt his payment from social tax. It is not difficult to assume that the position of representatives of the financial department in relation to personal income tax will be similar. Therefore, from the amount of payment for additional leave in excess of three days, income tax should also be withheld. individuals.
Example
According to the list approved by Kosmik LLC, the position of an employee of S. Kantov's company involves an irregular working day. In the form of compensation, the employee is entitled to 5 additional calendar days of vacation. These provisions are reflected in the collective agreement and the internal labor regulations of the company, as well as in the employment contract with Kantov.
After a year of work, Kantov went on vacation lasting 33 working days (28 days of the main vacation plus 7 days of additional). Based on the average daily earnings for the previous 12 months of work, equal to 517.23 rubles, the employee was accrued vacation pay in the amount of:
RUB 517.23 x 35 days = RUB 18,103.05
Of these, additional days of vacation had:
RUB 517.23 x 7 days = 3620.61 rubles.
The accountant of Cosmic included in tax expenses the full amount of vacation pay - both for the main and for additional leave; therefore, the amount of "excess" vacation pay (517.23 rubles x 4 days = 2068.92 rubles) must be included in the base for the UST, and in addition - in the base for personal income tax.
Many workers mistakenly believe that if they are constantly late at work, and their working day does not have a clear schedule, then it can be called irregular. In terms of meaning, it is possible, but according to the law, it will be considered as such if a corresponding entry is made in the employee’s employment contract, and additional social guarantees, due to employees with an official irregular day. Let's figure out what an irregular worker means in 2019 according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Changes and updates later in the article.
Flexible working hours, overtime work, as well as banal overtime at the will or whim of the employer have little in common with an irregular workday. In accordance with Art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which contains the corresponding concept, an irregular working day is a special mode of work when an employee remains to work after labor day not all the time, as is often the case Russian enterprises, but occasionally on the verbal command of the employer. Not any employee can be left “after work”, but only the one who occupies a position that, in accordance with the collective agreement or other regulatory act of the employer, is included in the list of positions with irregular working hours.
Flexible hours, irregular hours, overtime - what's the difference?
As mentioned above, many mistakenly take a flexible schedule for irregular working hours, when the employee works out the working time established by the employment contract without a fixed start and finish of the working day, which are determined by mutual agreement (Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, these are completely different things. Unlike a flexible work schedule, which is also fixed in an employment contract or an additional agreement to it, irregular working hours have clear boundaries. If it is written in the TD that the employee must start work at 10:00, then he cannot come to work at 12:00, since he has a position with an irregular working day. He must come at 10:00, otherwise he risks getting disciplinary action: remark or reprimand from the authorities (Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). And for being late for 4 hours or more, you can generally be fired.
Thus, an irregular working day, in contrast to a flexible schedule, has clear boundaries, but they can be “pushed apart” at the verbal request of the employer. Such requests may be episodic. The consent of the employee to work in excess of the normal working hours is not required, as well as additional payment.
In payment and in the need to obtain the consent of the employee for overtime lies the difference between an irregular working day and overtime work. Let's consider the difference in more detail.
Irregular working hours:
- does not require the consent of the person to involve him in work outside of working hours;
- not issued by order (a verbal order from the authorities is sufficient);
- payment for irregular working hours is not allowed;
- the number of episodic exits "after work" is not regulated;
- employees are entitled to leave for irregular working hours - the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 119) establishes guarantees in the form of at least three extra days holidays. Naturally paid. More may be specified in the employment or collective agreement. Days are required to be provided even if the employer did not use his right to occasionally involve the employee in labor duties at odd hours during the year.
Overtime in 2019:
- requires the mandatory consent of the employee, except in emergency cases;
- issued in writing by the employer;
- the duration of overtime work cannot exceed 4 hours for 2 consecutive days and 120 hours per year;
- paid at least one and a half times for the first 2 hours and at least
- twice in the following hours;
- no additional leave.
As can be seen from the comparison, on vacation, additional days for irregular working hours are relied upon, but overtime work is not relied upon. The opposite situation is with additional pay, which is made only for overtime work.

How is the irregular working day in 2019?
If an employee periodically performs work duties outside the established working hours, then this should be reflected in his employment contract (Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Appropriate notes are also made in the internal regulations of the enterprise, where the regulation on irregular working hours should be issued. worker, labor obligations which is stretched for a standard 8-hour working day or for a 10-12 hour work shift, do not neglect the official fixing of an irregular day. After all, in addition to the praise of the authorities, it also guarantees the employee an additional vacation for an irregular working day. This should also be written in the contract with the employee.
How many hours can be processed?
Lawyers are often asked the question: "Irregular working day - how many hours?". The Labor Code does not regulate irregular working hours by hours and does not explain how many hours in total an employer can involve an employee in irregular work. However, if the employer is too zealous in his right to involve the employee in the performance of duties outside the normal working hours (does this not occasionally, but on an ongoing basis), then this can be recognized as overtime work and “knock out” the due compensation. To do this, you will have to contact the state labor inspection and court. Such cases in judicial practice there is.
We hope that after reading this article about irregular working hours: “What does this mean?” - you don't ask anymore.
Recently, employers who have difficulties with working in irregular working hours have turned to us for clarification. The problem is that the latter sometimes start work later, for example, by a couple of hours, believing that lateness is acceptable, since in previous days there were delays at work after its formal end. And if they were often delayed, they demand a paid day off, indicating that they have already processed, and significantly. Is the position of employees justified, should the employer satisfy their requirements and provide an additional day off, how is work organized in the irregular working day? You will find answers to these and other questions in the article.
According to Art. 97 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer has the right, in the manner prescribed by the Labor Code, to involve the employee in work outside the working hours established for him:
- for overtime work (Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- if he works on an irregular working day (Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The concept of irregular working hours
Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives a clear definition of such a mode of work - this is a mode in which individual employees can, by order of the employer, if necessary, be occasionally involved in the performance of their labor functions outside the working hours established for them.In practice, personnel and accounting services often equate an irregular day with overtime work, but without providing appropriate guarantees.
Overtime work is carried out at the initiative of the employer outside the working hours established for the employee: daily work(shifts), and in the case of a summarized accounting of working time - in excess of the normal number of working hours for the accounting period (Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). That is, the concept of an irregular working day in the Labor Code involves the appointment special treatment working time. It is incorrect to equate this concept with overtime work.
Working in irregular working hours, like other employees, is subject to the mode of work in the organization. For example, if a company’s working day starts at 9.00 and ends at 18.00, then an employee with an irregular working day must come to work and leave it at specified time. The key point with an irregular working day is that the employee is involved in work in excess of the established norm of working hours sporadically, that is, not often. Although there are employers who are confident that if an employee has such a work schedule, he must sit at work from 8.00 to 00.00. This is mistake.
Many workers believe that since they have an irregular working day, they can come to work instead of the prescribed 9.00 to 10.00 or 11.00 or leave when they please. It's a delusion. The introduction of irregular working hours does not at all imply flexible working hours. Applying this mode to separate group persons does not release them from responsibility for non-compliance with labor discipline.
Thus, the employee filed a lawsuit to declare the disciplinary sanction unlawful. He was reprimanded for being 25 minutes late for work. The employee believed that there could be no delay, since he had an irregular working day. The court, recognizing the disciplinary sanction as lawful, pointed out that an irregular working day involves work outside the established working hours and does not provide for the release of the employee from work within the established working hours, as well as the arbitrary independent determination by the employee of the time of arrival and departure from work, the admission of being late for work(Determination of the Moscow City Court of June 7, 2016 No. 4g-5671/2016) .
Who can be assigned an irregular working day?
Let's say right away that the Labor Code does not limit the choice of the employer: he has the right to determine the categories of employees who can be established such a mode of work. The main condition is to develop and approve a list of employees' positions. It is included in the collective agreement, agreement or any local regulatory act of the employer.Such a list may include positions of employees:
- the duration of which cannot be accurately calculated (heads of companies, housekeeping staff and employees of technical services);
- planning the implementation of the tasks at their discretion;
- the working day of which is divided into intervals of unspecified duration.
Note
The list of positions of employees with irregular working hours must be agreed with the representative body of employees (if any).
Here is an example of what such a list might look like.
For work in irregular hours, employees holding the positions mentioned in clauses 1 and 2 are granted an additional annual paid leave of 5 calendar days in accordance with clause 3.7 of the internal labor regulations dated 10.10.2003 No. 3.
Is it possible to establish an irregular working day for a person performing work on a part-time basis?
Yes, you can. There is no corresponding ban, and Rostrud spoke out on this issue repeatedly, pointing out such a possibility (see, for example, Letter No. 1073-6-1 dated April 19, 2010).
Making a condition for irregular working hours
Many employers believe that if an employee is familiar with the local regulation, according to which his position implies a special mode of work, this is enough to periodically involve the employee in overtime work. Moreover, most employers prefer not to formalize the attraction in any way, making verbal orders. However, we will say right away that it is not enough to approve the list of positions of workers with irregular working hours. Any time an employee needs to work more than they should, this should be documented.So, if even before hiring it is known that this employee will need an irregular working day, before concluding an employment contract, a beginner must be familiarized with local regulations that establish a list of positions with irregular working hours, indicate the type and amount of compensation for work in this mode. Then an employment contract is drawn up, which includes a condition for working in irregular working hours, if the corresponding position is included in the list of positions of workers with irregular working hours. The inclusion of such a condition in the contract is necessary, since among the mandatory conditions of the employment contract, named in Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it means working time and rest time (if for this employee it differs from the general rules in force at this employer).
Thus, an employee was brought to disciplinary responsibility for refusing to continue working outside of working hours. Recognizing the punishment as unlawful, the court said that failure to comply with the oral order of the head of the department on the urgent processing of materials for the field season cannot serve as a basis for bringing to disciplinary liability in the form of a reprimand, even if the employment contract establishes irregular working hours (Appeal ruling of the Kurgan Regional Court dated 08.07 .2014 in case No. 33‑1982/2014).
After signing the employment contract, an order is issued, in which in the column "Conditions for employment, nature of work" an indication is made of a special mode of work. Next fill out employment history without specifying a special mode of operation, an employee's personal card.
If the position was included in the named list in the process of work, then the employees holding these positions must be notified in writing of the change in the mode of work at least two months before the establishment of a new mode. Because Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows you to change the terms of an employment contract only for reasons related to changes in organizational or technological conditions labor (changes in engineering and production technology, structural reorganization of production, etc.), the employer must have reasons to add this or that position to the list of positions with irregular working hours.
If the employee does not agree to work in the new conditions, the employer is obliged in writing to offer him another available job (as vacant position or a job corresponding to qualifications, and a vacant lower position or lower paying job), which the employee can perform taking into account his state of health.
In the absence of the specified work or refusal of the proposed employment contract is terminated in accordance with paragraph 7 of part 1 of Art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Registration of attraction to work over the norm of working hours
In the irregular working hours, the employee is involved in work periodically by order of the employer. However, in Art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not say how such an order should be drawn up. Based on this, we can say that the legislator also allows the oral form. At the same time, we believe that the oral form of the order should be used only if the company has a well-established time record.Regarding the fixation of processing in the irregular working hours, there are two positions.
Some experts believe that it is simply necessary to do this, since according to Part 4 of Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, each employer must keep accurate records of the working hours worked by each employee. For this, the time sheet is most often used. unified form T-12 or T-13. The use of magazines is also not prohibited.
If an employee is late after work, then, most likely, the employee who enters the information in the time sheet will go home earlier, so there will be no one to record the number of hours of processing. In such cases, it is advisable to issue a written order. In addition, it can be written in the job description or employment contract, for example, that an employee stays at work for two hours twice a month to prepare a report. But there is no need to fix the condition that it is required to linger daily or every other day. Otherwise, when an employee contacts the GIT, controllers recognize such periodic involvement in work outside of working hours as a violation of labor laws.
Other experts believe that an indication of the time sheet for processing leads to the fact that irregular working hours can be confused with overtime, and if the accountant considers the mark in the report card to be information about processing, he will pay for it.
We adhere to the first point of view, since no one canceled the time sheet. Yes, and fixing the time spent at work will help the employer track the frequency of going beyond the working day. In addition, time tracking will come in handy in case of any emergency - it will be possible to say for sure whether the employee was at the workplace or not.
note
Compensation for working irregular hours
As we found out, the processing time in the named mode of operation is not paid. However, legislators did not leave such workers without compensation.Article 119 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation determines that employees with irregular working hours are provided with annual additional paid leave, the duration of which is determined by a collective agreement or internal labor regulations and cannot be less than three calendar days. This leave can be added to the annual basic paid leave or taken separately.
note
The right to additional paid leave does not depend on whether the employee works overtime or goes home on time. If the employment contract reflects the condition of irregular working hours, then it will not be possible to avoid providing additional days of rest.
Sometimes employees, believing that they have overworked quite a lot (for example, worked outside of working hours every day for a month), ask the employer for an additional paid day off. Their desire is understandable - they thought that they would work sometimes, and the employer involved them in such work all the time. But overtime hours in irregular working hours are not equal to overtime hours, in which the employee has the right to choose additional rest time instead of increased pay (Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Since the legislation provides for only one type of compensation - additional leave, the employer is not obliged to satisfy such a request,
Attraction to work on holidays and weekends, to work at night
We repeat that many employers interpret Art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in their favor, believing that those working in irregular working hours should work "without days off and checkpoints." But given position wrong. All the norms of the Labor Code apply to workers in the named regime and they can be involved in work on a non-working holiday or day off only in compliance with the rules established by the code.For example, in order to attract employees with irregular working hours to work on a weekend, you will have to strictly follow Art. 113 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and issue:
- written agreement;
- taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization;
- notification of the right to refuse to work on a day off (for disabled people, women with children under the age of three) and familiarize employees with it against signature;
- order to work on a day off.
Finally, work on a day off must be paid according to the rules of Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Note
Work on a weekend or non-working holiday is paid at least twice the amount:
- pieceworkers - at least at double piecework rates;
- employees whose work is paid at daily and hourly tariff rates - in the amount of at least double the daily or hourly tariff rate;
- employees who receive a salary (official salary) - in the amount of at least a single daily or hourly rate (part of the salary (official salary) per day or hour of work) in excess of the salary (official salary), if the work was carried out within the monthly norm of working hours, and in the amount of at least double the daily or hourly rate (part of the salary (official salary) per day or hour of work) in excess of the salary (official salary), if the work was performed in excess of the monthly norm of working time.
Summarize
If necessary, the irregular working hours in the organization can be established for individual employees. At the same time, a list of positions for which such a mode of operation is applied must be determined by a local regulatory act. The condition on the mode of operation, which differs from that established in the organization, must be fixed in the employment contract.An irregular work schedule implies compliance with the established regime of work and rest at the enterprise, and, if necessary, an increase in the duration of work. Overtime is compensated by additional paid leave of at least three days.