GOST 61 75 acetic acid specifications.
GOST 61-75
INTERSTATE STANDARD
REAGENTS
ACETIC ACID
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
Decree State Committee standards of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated March 24, 1975 No. 724 date of introduction is set
01.04.75
The validity period was removed according to protocol No. 5-94 of the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (IUS 11-12-94)
This standard applies to the reagent - acetic acid, which is a clear, colorless, flammable liquid with a pungent odor, miscible with water, ethyl alcohol in any ratio.
The technical level indicators established by this standard are provided for the highest category quality.
The standard contains all the requirements of the SEV 5375-85 standard.
The standard does not provide for requirements for a “clean” qualification product, the standards for a number of indicators have been tightened, sections have been included: “Safety requirements” and “Manufacturer's guarantees” (see the appendix on the compliance of the requirements of this standard with the requirements of the CMEA standard).
Formula CH3COOH.
Molecular weight (according to international atomic masses 1971) - 60.05.
1. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
1.1. Acetic acid must be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to the technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
1.2. According to physico-chemical parameters, acetic acid must comply with the requirements and standards given in Table. .
Table 1
|
Chemically pure ice (chemically pure ice) |
Chemically pure (chemically pure) |
Net for analysis (analytical grade) |
|
|
OKP 26 3411 048308 |
OKP 26 3411 047310 |
OKP 26 3411 047200 |
|
|
1. Appearance |
Clear colorless liquid |
||
|
2. Mass fraction of acetic acid (CH3COOH), %, not less than |
|||
|
3. Crystallization temperature, °C |
Not standardized |
||
|
4. Mass fraction of non-volatile residue,%, no more |
|||
|
5. Mass fraction of sulfates (SO4),%, no more |
|||
|
6. Mass fraction of chlorides (Сl), %, no more |
|||
|
7. Mass fraction of iron (Fe),%, no more |
|||
|
8. Mass fraction of heavy metals (Pb),%, no more |
|||
|
9. Mass fraction of arsenic (As),%, no more |
|||
|
10. Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate in terms of oxygen (O),%, not more than |
|||
|
11. Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid (HCOOH),%, no more |
|||
|
12. Mass fraction of acetaldehyde (CH3CHO),%, no more |
|||
|
13. Mass fraction of acetic anhydride (CH3CO)2O, %, max |
Not standardized |
||
|
14. Dilution test |
Must pass the test of |
||
Notes:
1. If the mass fraction of acetic anhydride does not exceed 0.001%, the words “without anhydride” are added to the qualification of the reagent.
2. Acetic acid with the norms given in brackets is allowed to be produced until 01.01.95.
The maximum permissible concentration of acetic acid vapors in the air of the working area (MAC) is 5 mg/m3.
Determination of vapors of acetic acid in the air is carried out by the iodometric method.
If the maximum permissible concentration is exceeded, a pair of acetic acid acts irritatingly on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract; acetic acid also causes skin burns.
2a.2. When working with acetic acid, use individual means protection (filtering gas masks of grades B and BKF), as well as observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Do not allow acetic acid to enter the body.
First aid for burns - abundant washing with water.
2a.3. Acetic acid is a flammable liquid with a pungent, specific odor.
Boiling point, °C .............................................. ................... 118.1
Flash point of vapors, °C .............................................. ........ 38
Ignition temperature, °C .............................................. ........ 68
Self-ignition temperature, °C .............................................. 454
Ignition area, volume fraction, %:
lower limit................................................ .............................. 3.3
upper limit................................................ ........................... 22
Temperature limits of ignition, °C:
lower limit................................................ ................................... 35
upper limit................................................ ....................... 76
Category and group of explosive mixture of acetic acid vapors with air PA-T1 (GOST 12.1.011-78*).
* Within the territory of Russian Federation GOST R 51330.2-99, GOST R 51330.5-99, GOST R 51330.11-99, GOST R 51330.19-99 apply.
Work with acetic acid should be carried out away from fire. In case of fire, fire extinguishers should use PO-1D, PO-ZAI, Sampo foams, gas and powder compositions.
2a.4. Premises in which work with acetic acid is carried out must be equipped with general supply and exhaust mechanical ventilation.
The analysis of acetic acid should be carried out in a fume hood.
2.2. Determination of the content of sulfates, heavy metals, substances that reduce potassium permanganate, acetaldehyde and dilution tests is carried out by the manufacturer only at the request of the consumer and in the product intended for export.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3. METHODS OF ANALYSIS
3.1a. General instructions for the analysis - in accordance with GOST 27025-86.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 2).
rectified technical ethyl alcohol, the highest grade according to GOST 18300-87;
phenolphthalein (indicator) according to TU 6-09-5360-87, alcohol solution with a mass fraction of 1%, prepared according to GOST 4919.1-77;
equal-arm laboratory scales of the 2nd class model VLR-200 in accordance with GOST 24104-88 ** or any similar type with a division value of 0.0001 g.
3.2.2. Conducting an analysis
25 cm3 of distilled water are placed in a 100 cm3 conical flask with a ground stopper, weighed, 0.2 g of the product is added and the flask is weighed (the results of all weighings are recorded to the fourth decimal place), mixed thoroughly, titrated with sodium hydroxide solution in the presence of phenolphthalein to the appearance of a persistent slightly pink color of the solution.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.2.3. Results processing
Mass fraction of acetic acid ( X) as a percentage is calculated by the formula
where m- weight of the sample of the product, g;
V- volume of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol/dm3 (0.1 N) used for titration, cm3;
0.006005 - the amount of acetic acid corresponding to 1 cm3 of a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm3 (0.1 N), g.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.15% at confidence level P = 0,95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
The mass fraction of acetic acid in percent, depending on the crystallization temperature, is indicated in Table. .
table 2
|
Crystallization temperature, °C |
Mass fraction of acetic acid, % |
||
In case of disagreement in the assessment mass fraction acetic acid, as well as in the analysis of the product of qualification "x. h. ice”, the determination is carried out according to the crystallization temperature.
(Introduced additionally, Rev. No. 3).
3.3. Determination of crystallization temperature
The crystallization temperature of acetic acid is determined according to GOST 18995.5-73. In this case, preparation for analysis is carried out as follows: the device with the product is placed in a glass of water at a temperature of 5 °C - 7 °C. The product in the device is cooled to 10 ° C - 13 ° C and, without removing it from the glass, gently stir, without touching the bottom and walls of the test tube, until the first acid crystals appear.
At the moment of acid crystallization, the temperature rises sharply and, having reached a certain maximum, remains at this level for some time. For the crystallization temperature, noted with an error of 0.1 ° C, take the highest point of temperature rise.
It is allowed to carry out the determination by the thiocyanate method from 20.0 cm3 of a solution prepared according to p.
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the mass of iron does not exceed:
for the drug, chemically pure ice and chemically pure - 0.004 mg,
for the drug pure for analysis - 0.02 mg.
In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of iron, the determination is carried out by the photocolorimetric 2.2"-dipyridyl method.
3.5 - 3.7. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the observed color of the analyzed solution is not more intense than the color of the solution prepared simultaneously with the analyzed and containing in the same volume:
for chemically pure ice product - 0.01 mg Pb,
for chemically pure product - 0.01 mg Pb,
for product pure for analysis - 0.02 mg Pb
and the same amount of reagents.
It is allowed to carry out the determination from the corresponding volume of the solution prepared according to paragraph after neutralizing it with an ammonia solution.
In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of heavy metals, the determination is carried out by the hydrogen sulfide method.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.9. Determination of the mass fraction of arsenic
In this case, preparation for the analysis is carried out as follows:
10.00 g (9.5 cm3) of the analyzed product, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in the flask of the device for determining the arsenic content, 30 cm3 of distilled water, 20 cm3 of an acid solution, 1 cm3 of a stannous chloride solution are added, mixed and then the determination is carried out according to GOST 10485-75.
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the observed color of the bromine-mercury paper of the analyzed solution is not more intense than the color of the bromine-mercury paper of the solution prepared simultaneously with the analyzed and containing in the same volume:
for chemically pure ice product - 0.0015 mg As,
for a chemically pure product - 0.005 mg As,
for a product pure for analysis - 0.005 mg As
and the same amount of reagents.
3.10. Determination of the mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate in terms of oxygen (O)
3.10.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.10.2. Conducting an analysis
10.00 g (9.5 cm3) of the analyzed product, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in a conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 500 cm3, 10 cm3 of sulfuric acid are added, the solution is cooled to 18 ° C - 20 ° C, 1 cm3 of a solution of dichromic acid potassium and mix.
Simultaneously prepare a control solution under the same conditions, with the same amounts of reagents and solutions.
The analyzed and control solutions are left for 30 minutes. Then, 50 cm3 of distilled water are added to both solutions, mixed, cooled to 18 ° C - 20 ° C, 10 cm3 of potassium iodide solution are added, closed with a cork, mixed and left in a dark place for 10 minutes. The cork, neck and walls of the flask are washed off with 150 cm3 of distilled water and the released iodine is titrated from a microburette with a solution of sodium sulphate in the presence of starch until the solution becomes colorless.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.10.3. Results processing
The mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate, in terms of oxygen ( X 2), as a percentage is calculated by the formula
![]()
where m- weight of the sample of the product, g;
V- the volume of sodium sulphate solution with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol/dm3, used for titration of the control solution, cm3;
V 1 - volume of sodium sulphate solution with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol/dm3, used for titration of the analyzed product, cm3;
0.0008 - the amount of oxygen corresponding to 1 cm3 of a solution of potassium dichromate with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm3, g.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.001% with a confidence level P = 0,95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.11. Determination of the mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid
3.11.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.11.2. Conducting an analysis
10 g (9.5 cm3) of the product to be analyzed, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in a 250 cm3 conical flask with a ground stopper containing 70 cm3 of water. 15 cm3 of a sulfuric acid solution, 50 cm3 of a potassium permanganate solution are added to the solution and heated in a thermostat at 80 °C for 15 minutes. The flask is cooled for 10 minutes with running water, 2 g of potassium iodide are added and left alone for 5 minutes. The released iodine is titrated with a solution of sodium sulphate, and 2 cm3 of starch solution are added at the end of the titration.
At the same time, a control solution is prepared under the same conditions with the same amounts of reagents and solutions as in the analyzed solution.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.11.3. Results processing
Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid ( X 3), as a percentage, is calculated by the formula
![]()
where m- weight of the sample of the product, g;
V 1 - volume of sodium sulphate solution with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol/dm3, used for titration in the control solution, cm3;
V- volume of sodium sulphate solution with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol/dm3, used for titration of the analyzed product, cm3;
0.00023 - the amount of formic acid corresponding to 1 cm3 of a solution of potassium permanganate with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol / dm3, g.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.0005% with a confidence level P = 0,95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.12. Determination of the mass fraction of acetaldehyde (CH3CHO)
nozzle H 1 29/32-14/23-14/23 or bend I< 750 ° 2К 29/32-14/23 по ГОСТ 25336-82 ;
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the mass of acetaldehyde does not exceed:
for chemically pure ice product - 0.2 mg,
for chemically pure product - 0.4 mg,
for a product pure for analysis - 0.6 mg.
(Changed edition, Rev. No. 2, 3).
3.13. Determination of the mass fraction of acetic anhydride
3.13.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
pipettes 2-2-25 (or 2-2-50 or 2-2-5), 2-2-10 according to GOST 29169-91.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.13.2. Conducting an analysis
25 cm3 of the product are placed in a dry conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 100 cm3, 10 cm3 of aniline solution are added, closed with a stopper, mixed and incubated for 10 minutes. Then add one drop of crystal violet solution and titrate with perchloric acid until the color changes to green. Simultaneously prepare a control solution under the same conditions, with the same amounts of reagents and solutions.
If, during back titration, a change in the color of the analyzed solution occurs from a few drops of perchloric acid solution, which indicates that the mass fraction of acetic anhydride in the analyzed product is more than 0.03%, then an additional amount of aniline should be added to the control solution and the exposure should be allowed again for 10 minutes.
If the mass fraction of acetic anhydride in the analyzed product is less than 0.005%, 50 cm3 of the product is taken for determination, if the mass fraction is more than 0.05%, 5 cm3 or 10 cm3 of the product are taken.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.13.3. Results processing
Mass fraction of acetic anhydride ( X 4) as a percentage calculated by the formula
![]()
where V- the volume of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol/dm3, used for titration in the control solution, cm3;
V 1 - volume of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol/dm3, used for titration of the analyzed product, cm3;
0.0102 - the amount of acetic anhydride corresponding to 1 cm3 of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm3, g;
1.0498 - density of acetic acid, g/cm3.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.002% with a confidence level P= 0,95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
Type and type of container: 3-1, 3-2, 3-5, 3-8, 8-1, 8-2, 8-5, 9-1, 10-1.
Packing group: V, VI, VII.
For packing containers with acetic acid, wood chips impregnated with solutions are used. calcium chloride, magnesium chloride or ammonium sulphate, as well as slag wool or other non-combustible sealing material.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
4.2. A danger sign is applied to the container according to GOST 19433-88 (class 8, subclass 8.1, drawing 8 - main, drawing 3 - additional, classification code 8142, UN serial number 2789).
4.3. The product is transported by all modes of transport in accordance with the rules for the transport of flammable goods.
4.4. The product is stored in closed containers in rooms specially adapted for the storage of flammable substances, protected from direct sunlight and precipitation.
Established standards for qualifying clean
Mass fraction of acetic acid, %, not less than for qualifications:
X. h. ice 99.8
X. h. ice 99.8 (99.5)
X. hours 99.5 (99.0)
h.d.a. 99.5
h.d.a. 99 (98)
Mass fraction of sulfates, %, not more than for qualification
X. h. ice 0.0001
X. h. ice 0.0002
Mass fraction of iron, %, no more than for qualifications:
X. h. ice 0.00002
X. h. ice 0.00002 (0.00005)
X. hours 0.00002 (0.00005)
Mass fraction of heavy metals, %, not more than for qualifications:
X. h. ice 0.00003
X. h. ice 0.00005
X. hours 0.00005 (0.00008)
Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate,%, not more than for qualification
X. h. ice 0.003
X. h. ice 0.003 (0.005)
The determination is carried out from a sample of the product. It is allowed to determine the mass fraction of heavy metals from the solution obtained when determining the mass fraction of non-volatile residue
The determination is carried out from the solution obtained in the determination of non-volatile residue
"Safety requirements"
Missing
"Manufacturer's warranty"
Established standards for qualifying clean
Mass fraction of acetic acid, %, not less than for qualifications:
X. h. ice 99.8
X. h. ice 99.8 (99.5)
X. hours 99.5 (99.0)
h.d.a. 99.5
h.d.a. 99 (98)
Mass fraction of sulfates, %, not more than for qualification
X. h. ice 0.0001
X. h. ice 0.0002
Mass fraction of iron, %, no more than for qualifications:
X. h. ice 0.00002
X. h. ice 0.00002 (0.00005)
X. hours 0.00002 (0.00005)
Mass fraction of heavy metals, %, not more than for qualifications:
X. h. ice 0.00003
X. h. ice 0.00005
X. hours 0.00005 (0.00008)
Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate,%, not more than for qualification
X. h. ice 0.003
X. h. ice 0.003 (0.005)
The determination is carried out from a sample of the product. It is allowed to determine the mass fraction of heavy metals from the solution obtained when determining the mass fraction of non-volatile residue
The determination is carried out from the solution obtained in the determination of non-volatile residue
"Safety requirements"
Missing
"Manufacturer's warranty"
INTERSTATE STANDARD
REAGENTS
ACETIC ACID
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
Official edition
Standartinform
INTERSTATE STANDARD
Reagents
ACETIC ACID
Specifications
reagents. Acetic acids. Specifications
Instead of GOST 61-69
MKS 71.040.30 OKP 26 3411 0470 02
By the Decree of the State Committee of Standards of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated March 24, 1975 No. 724, the introduction date was set
The validity period was removed according to protocol No. 5-94 of the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (IUS 11-12-94)
This standard applies to the reagent - acetic acid, which is a clear, colorless, flammable liquid with a pungent odor, miscible with water, ethyl alcohol in any ratio.
The technical level indicators established by this standard are provided for the highest quality category.
The standard contains all the requirements of the SEV 5375-85 standard.
The standard does not provide for requirements for a “clean” qualification product, the standards for a number of indicators have been tightened, sections have been included: “Safety requirements” and “Manufacturer's guarantees” (see the appendix on the compliance of the requirements of this standard with the requirements of the CMEA standard).
Formula CH 3 COOH.
Molecular weight (according to international atomic masses 1971) - 60.05.
1. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
1.1. Acetic acid must be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to the technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
1.2. According to physico-chemical parameters, acetic acid must comply with the requirements and standards given in Table. one.
Edition official reprint forbidden
Edition (October 2006) with Amendments No. 1, 2, 3, approved in March 1978, December 1979, October 1986 (IUS 3-78, 2-80, 1-87).
© Standards Publishing House, 1975 © Standartinform, 2006
Table 1
|
Name of indicator |
Chemically pure ice (chemically pure ice) |
Chemically pure (chemically pure) |
Net for analysis (analytical grade) |
|
OKP 26 3411 048308 |
OKP 26 3411 047310 |
OKP 26 3411 047200 |
|
|
1. Appearance |
Clear colorless liquid |
||
|
2. Mass fraction of acetic acid (CH 3 COOH),%, not less than | |||
|
3. Crystallization temperature, °C |
Not standardized |
||
|
4. Mass fraction of non-volatile residue,%, no more | |||
|
5. Mass fraction of sulfates (S0 4),%, no more | |||
|
6. Mass fraction of chlorides (C1),%, no more | |||
|
7. Mass fraction of iron (Eu),%, no more | |||
|
8. Mass fraction of heavy metals (Pb),%, no more | |||
|
9. Mass fraction of arsenic (As),%, no more | |||
|
10. Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate in terms of oxygen (O),%, not more than | |||
|
11. Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid | |||
|
(НСООН), %, no more 12. Mass fraction of acetaldehyde (CH 3 CHO),%, no more | |||
|
13. Mass fraction of acetic anhydride (CH 3 C0) 2 0,%, no more |
Not standardized |
||
|
14. Dilution test |
Must pass the test according to clause 3.14 |
||
Notes:
1. If the mass fraction of acetic anhydride does not exceed 0.001%, the words “without anhydride” are added to the qualification of the reagent.
2. Acetic acid with the norms given in brackets is allowed to be produced until 01.01.95.
Sec. 1. (Changed edition, Rev. No. 3).
2a. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
2a. 1. Acetic acid belongs to the 3rd hazard class according to GOST 12.1.007-76.
The maximum permissible concentration of acetic acid vapors in the air of the working area (MAC) is 5 mg/m 3 .
Determination of vapors of acetic acid in the air is carried out by the iodometric method.
When the maximum permissible concentration is exceeded, a pair of acetic acid acts irritatingly on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract; acetic acid also causes skin burns.
2a.2. When working with acetic acid, you should use personal protective equipment (filtering gas masks of grades B and BKF), as well as observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Do not allow acetic acid to enter the body.
First aid for burns - abundant washing with water.
2a. 3. Acetic acid is a flammable liquid with a sharp specific odor.
Boiling point, °C.........
Flash point of vapors, °С......
Ignition temperature, °С......
Self-ignition temperature, °С. . . . Ignition area, volume fraction, %:
lower limit............
upper limit............
Temperature limits of ignition, °С:
lower limit.......................35
upper limit............................76
Work with acetic acid should be carried out away from fire. In case of fire, fire extinguishers should use PO-1D, PO-ZAI, Sampo foams, gas and powder compositions.
2a.4. Premises in which work with acetic acid is carried out must be equipped with general supply and exhaust mechanical ventilation.
The analysis of acetic acid should be carried out in a fume hood.
Sec. 2a.
2. ACCEPTANCE RULES
2.1. Acceptance rules - according to GOST 3885-73.
2.2. Determination of the content of sulfates, heavy metals, substances that reduce potassium permanganate, acetaldehyde and dilution tests is carried out by the manufacturer only at the request of the consumer and in the product intended for export.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3. METHODS OF ANALYSIS
3.1a. General instructions for the analysis - in accordance with GOST 27025-86.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 2).
3.1. Samples are taken according to GOST 3885-73. The mass of the average sample must be at least 2 kg (1.9 dm 3).
3.2a. Appearance definition
Appearance is determined at 20 °C visually by comparison with distilled water according to GOST 14871-76. In this case, the analyzed product should not have opalescence and should not contain mechanical particles.
(Introduced additionally, Rev. No. 3).
3.2. Determination of the mass fraction of acetic acid by alkalimetric titration
3.2.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
Distilled water, not containing carbon dioxide; prepared according to GOST 4517-87;
sodium hydroxide according to GOST 4328-77, concentration solution c (NaOH)=0.l mol/dm 3 (0.1 i.), prepared according to GOST 25794.1-83;
rectified technical ethyl alcohol, the highest grade according to GOST 18300-87;
phenolphthalein (indicator) according to TU 6-09-5360-87, alcohol solution with a mass fraction of 1%, prepared according to GOST 4919.1-77;
burette 1-2-50 according to GOST 29252-91;
flask Kn-1-100-14/23 according to GOST 25336-82;
cylinder 1-25 according to GOST 1770-74;
equal-arm laboratory scales of the 2nd class model VLR-200 in accordance with GOST 24104-88 ** or any similar type with a division value of 0.0001 g.
3.2.2. Conducting an analysis
25 cm 3 of distilled water are placed in a conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 100 cm 3, weighed, 0.2 g of the product is added and the flask is weighed (the results of all weighings are recorded to the fourth decimal place), mixed thoroughly, titrated with sodium hydroxide solution in the presence of phenolphthalein until a persistent slightly pink color of the solution appears.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
* GOST R 51330.2-99, GOST R 51330.5-99, GOST R 51330.11-99, GOST R 51330.19-99 are valid on the territory of the Russian Federation.
3.2.3. Results processing
The mass fraction of acetic acid (X) as a percentage is calculated by the formula
„V- 0.006005 100
V is the volume of a solution of sodium hydroxide with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 (0.1 N.) used for titration, cm 3;
0.006005 - the amount of acetic acid corresponding to 1 cm 3 of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 (0.1 n.), g.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.15% with a confidence level P = 0.95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.3a. Determination of the mass fraction of acetic acid by crystallization temperature
The definition is carried out according to and. 3.3 of this standard and according to GOST 18995.5-73.
The mass fraction of acetic acid in percent, depending on the crystallization temperature, is indicated in Table. 2.
table 2
In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of acetic acid, as well as in the analysis of the product of the qualification “x. h. ice”, the determination is carried out according to the crystallization temperature.
(Introduced additionally, Rev. No. 3).
3.3. Determination of crystallization temperature
The crystallization temperature of acetic acid is determined according to GOST 18995.5-73. In this case, preparation for analysis is carried out as follows: the device with the product is placed in a glass of water at a temperature of 5 °C-7 °C. The product in the device is cooled to 10 °C-13 °C and, without removing it from the glass, gently stir, without touching the bottom and walls of the test tube, until the first acid crystals appear.
At the moment of acid crystallization, the temperature rises sharply and, having reached a certain maximum, remains at this level for some time. For the crystallization temperature, marked with an error of 0.1 ° C, take the highest point of temperature rise.
3.4. Determination of the mass fraction of non-volatile residue
The determination is carried out according to GOST 27026-86 from a volume of 95 cm 3 (100 g) in a quartz or platinum cup.
The residue is dissolved in 1 cm 3 of a hydrochloric acid solution (GOST 3118-77) with a mass fraction of 25% and 15 cm 3 of water, the solution is quantitatively transferred into a volumetric flask with a capacity of 100 cm 3 (GOST 1770-74), the volume of the solution is adjusted to the mark with water and mixed. The solution is kept to determine the mass fraction of iron and heavy metals.
3.4.1, 3.4.2. (Deleted, Rev. No. 2).
3.5. Determination of the mass fraction of sulfates
The determination is carried out according to GOST 10671.5-74. At the same time, preparation for analysis is carried out: 50.0 g (47.6 cm 3) of the analyzed product is placed in a platinum or quartz cup, 0.2 g of sodium carbonate (GOST 83-79) is added and evaporated to dryness. Residue after evaporation
diluted in 15 cm 3 of water (if necessary, the solution is filtered through a dense ash-free filter) and the volume of the solution is adjusted to 20 cm 3.
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the opalescence of the analyzed solution observed after 30 minutes on a dark background is not more intense than the opalescence of the reference solution prepared simultaneously with the analyzed one and containing in the same volume:
for the product chemically pure ice and chemically pure - 0.05 mg S0 4, for the product pure for analysis - 0.10 mg S0 4.
It is allowed to carry out the determination by the visual-nephelometric method without evaporation using a seed solution. At the same time, 10.0 g (9.5 cm 3) of the analyzed product is placed in a conical flask with a capacity of 50 cm 3 (GOST 25336-82), diluted with water to 37 cm 3, 3 cm 3 of a gelatin solution is added, measured with a pipette with a capacity of 10 cm 3 (GOST 29169-91) and mix. Separately, 0.1 cm 3 of a solution containing 0.001 mg of S0 4 is placed in a test tube, 1 cm 3 of a solution of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of (HC1) \u003d 1 mol / dm 3, 3 cm 3 of a solution of barium chloride, measured with a pipette, are added, and shaken for 1 minute. Then the contents of the test tube are poured into the analyzed solution, the test tube is rinsed with a small volume of water into the flask, the volume of the solution in the flask is adjusted with water to 50 cm 3 and mixed.
The opalescence of the analyzed solution observed after 1 hour should not be more intense than the opalescence of the reference solution prepared simultaneously in the same way and containing in the same volume:
for the product chemically pure ice and chemically pure - 0.01 mg S0 4, for the product pure for analysis - 0.02 mg S0 4
and the same volumes of solutions of hydrochloric acid, gelatin and barium chloride.
In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of sulfates, the determination is carried out by the method of evaporating the product in the presence of sodium carbonate and using a seed solution.
3.6. Determination of the mass fraction of chlorides
The determination is carried out according to GOST 10671.7-74 visual nephelometric method in a volume of 40 cm 3 with the addition of 2 cm 3 nitric acid solution.
The weighed weight of the product is 10.00 g (corresponds to 9.5 cm 3).
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the opalescence of the analyzed solution observed after 10 minutes on a dark background is not more intense than the opalescence of the reference solution prepared simultaneously with the analyzed one and containing in the same volume:
for a product chemically pure ice and chemically pure - 0.01 mg C1, for a product pure for analysis - 0.02 mg C1 and the same amounts of reagents.
3.7. Determination of the mass fraction of iron
The determination is carried out according to GOST 10555-75 2.2 "-dipyridyl method. In this case,
20.0 cm 3 of the solution obtained according to clause 3.4 (corresponding to 20.00 g of the analyzed product), measured with a pipette with a capacity of 20 cm 3 (GOST 29169-91).
It is allowed to carry out the determination by the thiocyanate method from 20.0 cm 3 of a solution prepared according to clause 3.4, or by the 1,10-phenanthroline method without preliminary evaporation of 20.00 g of the sample of the analyzed product (corresponding to 19.0 cm 3).
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the mass of iron does not exceed:
for the drug chemically pure ice and chemically pure - 0.004 mg, for the drug pure for analysis - 0.02 mg.
In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of iron, the determination is carried out by the photocolorimetric 2.2 "-dipyridyl method.
3.5-3.7. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.8. Determination of the mass fraction of heavy metals
The determination is carried out according to GOST 17319-76 by the thioacetamide visual-colorimetric or hydrogen sulfide method.
At the same time, preparation for analysis is carried out: 33.40 g (32.0 cm 3) of acetic acid of chemically pure glacial qualification or 20.00 g (19.0 cm 3) of acetic acid of chemically pure and pure qualification for analysis, measured to within first decimal place, placed in quartz
vuyu or porcelain cup and evaporated to dryness in a water bath. 10 cm 3 of distilled water are added to the residue, and then the determination is carried out according to GOST 17319-76.
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the observed color of the analyzed solution is not more intense than the color of the solution prepared simultaneously with the analyzed solution and containing in the same volume: for the chemically pure ice product - 0.01 mg Pb, for the chemically pure product - 0.01 mg Pb, for a product pure for analysis - 0.02 mg Pb and the same amounts of reagents.
It is allowed to carry out the determination from the corresponding volume of the solution prepared according to and. 3.4 after neutralization with ammonia solution.
In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of heavy metals, the determination is carried out by the hydrogen sulfide method.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.9. Determination of the mass fraction of arsenic
The determination is carried out according to GOST 10485-75.
In this case, preparation for the analysis is carried out as follows:
10.00 g (9.5 cm 3) of the analyzed product, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in a flask of an instrument for determining the arsenic content, 30 cm 3 of distilled water, 20 cm 3 of an acid solution, 1 cm 3 of a tin dichloride solution are added, mixed and then the determination is carried out according to GOST 10485-75.
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the observed color of the bromine-mercury paper of the analyzed solution is not more intense than the color of the bromine-mercury paper of the solution prepared simultaneously with the analyzed and containing in the same volume:
for a chemically pure ice product - 0.0015 mg As, for a chemically pure product - 0.005 mg As, for a pure product for analysis - 0.005 mg As and the same amounts of reagents.
(Changed edition, Rev. No. 2, 3).
3.10. Determination of the mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate in terms of oxygen (O)
3.10.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
potassium dichromate according to GOST 4220-75, a concentration solution with 0 / ^ KjCrjOj ^ O, I mol / dm 3 (0.1 N), prepared according to GOST 25794.2-83;
potassium iodide according to GOST 4232-74, solution with a mass fraction of 20%; sulfuric acid according to GOST 4204-77, x. hours;
soluble starch according to GOST 10163-76, solution with a mass fraction of 0.5%; sodium sulphate (sodium thiosulfate) 5-water according to GOST 27068-86 concentrations with (Na 2 S 2 O3-5H 2 O) \u003d 0.l mol / dm 3 (0.1 N), prepared according to GOST 25794.2-83; burette 6-2-2 according to GOST 29252-91; flask Kn-1-500-29/32 according to GOST 25336-82; pipettes 6-2-10 and 2-2-1 according to GOST 29169-91; cylinder 1-250 according to GOST 1770-74.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.10.2. Conducting an analysis
10.00 g (9.5 cm 3) of the analyzed product, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in a conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 500 cm 3, 10 cm 3 of sulfuric acid are added, the solution is cooled to 18 ° C-20 ° C, add 1 cm 3 of potassium dichromate solution and mix.
Simultaneously prepare a control solution under the same conditions, with the same amounts of reagents and solutions.
The analyzed and control solutions are left for 30 minutes. Then, 50 cm 3 of distilled water are added to both solutions, mixed, cooled to 18 ° C-20 ° C, 10 cm 3 of potassium iodide solution are added, closed with a cork, mixed and left in a dark place for 10 minutes. The cork, neck and walls of the flask are washed off with 150 cm 3 of distilled water and highlighting
iodine is titrated from a microburette with a solution of sodium sulphate in the presence of starch until the solution becomes colorless.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.10.3. Results processing
The mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate, in terms of oxygen (X 2), as a percentage, is calculated by the formula
„ (V-V0- 0.0008 100
where t is the mass of the sample of the product, g;
V is the volume of a solution of sodium sulphate with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 used for titration of the control solution, cm 3;
V\ - the volume of a solution of sodium sulphate with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 used for titration of the analyzed product, cm 3;
0.0008 - the amount of oxygen corresponding to 1 cm 3 of a solution of potassium dichromate with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3, g.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.001% at a confidence level P = 0.95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.11. Determination of the mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid
3.11.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
Distilled water according to GOST 6709-72, distilled in the presence of potassium permanganate;
potassium iodide according to GOST 4232-74;
potassium permanganate according to GOST 20490-75, concentration solution c (1/5 KMp0 4) = = 0.01 mol / dm 3 (0.01 i.), freshly prepared, prepared according to GOST 25794.2-83;
sulfuric acid according to GOST 4204-77, solution with a mass fraction of 16%;
soluble starch according to GOST 10163-76, aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 1%;
sodium sulphate (sodium thiosulfate), 5-water according to GOST 27068-86, concentration solution c (Na 2 S 2 03-5H 2 0) \u003d 0.01 mol / dm 3 (0.01 i.) freshly prepared, prepared according to GOST 25794.2-83;
flask Kn-1-250-29/32 according to GOST 25336-82;
pipettes 6-2-10, 2-2-50, 4-2-2 according to GOST 29169-91;
cylinder 1-100 according to GOST 1770-74.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.11.2. Conducting an analysis
10 g (9.5 cm 3 ) of the product to be analyzed, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in a 250 cm 3 conical flask with a ground stopper containing 70 cm 3 of water. 15 cm 3 of a sulfuric acid solution, 50 cm 3 of a potassium permanganate solution are added to the solution and heated in a thermostat at 80 ° C for 15 minutes. The flask is cooled for 10 minutes with running water, 2 g of potassium iodide are added and left alone for 5 minutes. The released iodine is titrated with a solution of sodium sulphate, and 2 cm 3 of a starch solution are added at the end of the titration.
At the same time, a control solution is prepared under the same conditions with the same amounts of reagents and solutions as in the analyzed solution.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.11.3. Results processing
The mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid (X 3), in percent, is calculated by the formula
„ (F! - K) 0.00023 100
where t is the mass of the sample of the product, g;
V\ - the volume of a solution of sodium sulphate with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol / dm 3 used for titration in the control solution, cm 3;
V is the volume of a solution of sodium sulphate with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol/dm 3 used for titration of the analyzed product, cm 3 ;
0.00023 - the amount of formic acid corresponding to 1 cm 3 of a solution of potassium permanganate with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol / dm 3, g.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.0005% at a confidence level P = 0.95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
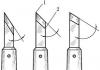
3.12. Determination of the mass fraction of acetaldehyde (CH 3 CHO)
The determination is carried out according to GOST 16457-76 by photometric or visual-colorimetric method. At the same time, a device for the determination of acetaldehyde is assembled (see drawing), consisting of: a flask OG-2-500-29/32 or KGU-2-1-500-29/32 according to GOST 25336-82; nozzle H 1 29/32-14/23-14/23 or bend I< 750 ° 2К 29/32-14/23 по ГОСТ 25336-82; воронки ВК-50 ХС по ГОСТ 25336-82; холодильника ХПТ 1-100-14/23 по ГОСТ 25336-82; цилиндра 2-50 по ГОСТ 1770-74;
along AIO-14/23-14/23-60 in accordance with GOST 25336-82, elongated with a glass tube;
20.00 g (19.0 cm 3) of the analyzed product, measured with a pipette with a capacity of 25 cm 3 (GOST 29169-91) with an accuracy of the first decimal place, is placed in the dropping funnel of the device.
Device for the determination of acetaldehyde (scheme)

Several glass capillaries fused at one end are introduced into the flask of a distillation device with a capacity of 500 cm 3, and about 40 cm 3 of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass fraction of 30% (GOST 4328-77) is poured. The number of milliliters of sodium hydroxide required to neutralize 20 g of the product is preliminarily determined in a separate experiment by appropriate titration in the presence of universal indicator paper to pH 7.
The flask with the contents is closed with a stopper, through which the end of the refrigerator tube with a spray trap and the end of the dropping funnel are passed. The other end of the refrigerator tube should be slightly immersed in water (5 cm 3) contained in a cylinder marked with 5 and 15 cm 3. From the dropping funnel, the product is poured into the flask, then 2-3 drops of an alcohol solution of phenolphthalein with a mass fraction of 0.1%, prepared according to GOST, are introduced into the flask of the device through the funnel
4919.1-77. If necessary, neutralize the contents of the flask with the product or sodium hydroxide solution, adding it dropwise to a faint pink color. The tap of the dropping funnel is closed and when heated, 10 cm 3 of liquid is distilled into the receiver, closing it with a ground stopper, mixed, the volume of the solution is adjusted to 23 cm 3 with water, and then the determination is carried out according to GOST 16457-76.
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the mass of acetaldehyde does not exceed:
for a chemically pure ice product - 0.2 mg, for a chemically pure product - 0.4 mg, for a product pure for analysis - 0.6 mg.
(Changed edition, Rev. No. 2, 3).
3.13. Determination of the mass fraction of acetic anhydride
3.13.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
Aniline according to GOST 5819-78, freshly distilled, solution with a mass fraction of 0.5% in acetic acid, x. h. ice-cold without anhydride, suitable for use within 15-20 days when stored in a dark bottle with a ground stopper;
crystal violet (indicator), solution with a mass fraction of 0.5% in acetic acid, x. h. ice without anhydride;
acetic acid, x. h. icy without anhydride;
perchloric acid, acetic acid solution of concentration c (NSYu 4) \u003d 0.1 mol / dm 3 (0.1 i.); prepared according to GOST 25794.3-83;
burette 7-2-10 according to GOST 29252-91; flask Kn-1-100-14/23 according to GOST 25336-82;
pipettes 2-2-25 (or 2-2-50 or 2-2-5), 2-2-10 according to GOST 29169-91.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.13.2. Conducting an analysis
25 cm 3 of the product are placed in a dry conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 100 cm 3 , 10 cm 3 of an aniline solution are added, closed with a stopper, mixed and incubated for 10 minutes. Then add one drop of crystal violet solution and titrate with perchloric acid until the color changes to green. Simultaneously prepare a control solution under the same conditions, with the same amounts of reagents and solutions.
If, during back titration, a change in the color of the analyzed solution occurs from a few drops of perchloric acid solution, which indicates that the mass fraction of acetic anhydride in the analyzed product is more than 0.03%, then an additional amount of aniline should be added to the control solution and the exposure should be allowed again for 10 minutes.
If the mass fraction of acetic anhydride in the analyzed product is less than 0.005%, 50 cm 3 of the product are taken for determination, if the mass fraction is more than 0.05%, 5 cm 3 or 10 cm 3 of the product are taken. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.13.3. Results processing
The mass fraction of acetic anhydride (X 4) as a percentage is calculated by the formula
„ (V-Vi) - 0.0102 100
where V is the volume of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 used for titration in the control solution, cm 3;
Fj is the volume of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol/dm 3 used for titration of the analyzed product, cm 3 ;
0.0102 - the amount of acetic anhydride corresponding to 1 cm 3 of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3, g;
1.0498 - density of acetic acid, g/cm 3 .
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.002% at a confidence level P = 0.95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.14. dilution test
10 cm 3 of the product is diluted with 30 cm 3 of distilled water (GOST 6709-72) and mixed. The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the solution remains clear for 1 h.
4. PACKAGING, LABELING, TRANSPORT AND STORAGE
4.1. Packaging and labeling - in accordance with GOST 3885-73.
Type and type of container: 3-1, 3-2, 3-5, 3-8, 8-1, 8-2, 8-5, 9-1, 10-1.
Packing group: V, VI, VII.
For packing containers with acetic acid, wood shavings impregnated with solutions of calcium chloride, magnesium chloride or ammonium sulphate, as well as slag wool or other non-combustible sealing material, are used.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
4.2. A danger sign is applied to the container according to GOST 19433-88 (class 8, subclass 8.1, drawing 8 - main, drawing 3-additional, classification code 8142, UN serial number 2789).
4.3. The product is transported by all modes of transport in accordance with the rules for the transport of flammable goods.
4.4. The product is stored in closed containers in rooms specially adapted for the storage of flammable substances, protected from direct sunlight and precipitation.
5. MANUFACTURER WARRANTY
5.1. The manufacturer guarantees the compliance of acetic acid with the requirements of this standard, subject to the conditions of transportation and storage.
5.2. Guaranteed shelf life of the product is one year from the date of manufacture.
Sec. 5. (Changed edition, Rev. No. 3).
Sec. 6. (Deleted, Rev. No. 3).
APPENDIX
Mandatory
Compliance with the requirements of GOST 61-75 ST SEV 5375-85
|
ST SEV 5375-85 |
|||
|
There are no standards for qualification |
Established standards for qualification |
||
|
Mass fraction of acetic acid, %, not | |||
|
less for qualifications: |
less for qualifications: |
||
|
X. h. ice 99.8 |
X. h. ice 99.8 (99.5) |
||
|
X. hours 99.5 (99.0) |
|||
|
h.d.a. 99.5 |
h.d.a. 99 (98) |
||
|
Mass fraction of sulfates, %, no more | |||
|
for qualification |
qualifications |
||
|
X. h. ice 0.0001 |
X. h. ice 0.0002 |
||
|
Mass fraction of iron, %, not more than for | |||
|
qualifications: |
qualifications: |
||
|
X. h. ice 0.00002 |
X. h. ice 0.00002 (0.00005) |
||
|
X. hours 0.00002 (0.00005) |
|||
|
Mass fraction of heavy metals, %, not | |||
|
more for qualifications: |
more for qualifications: |
||
|
X. h. ice 0.00003 |
X. h. ice 0.00005 |
||
|
X. hours 0.00005 (0.00008) |
|||
|
Mass fraction of substances, restoring- | |||
|
permanganate potassium,%, not more |
potassium permanganate, %, no more |
||
|
more for qualification |
for qualification |
||
|
X. h. ice 0.003 |
X. h. ice 0.003 (0.005) |
||
|
The determination is carried out from a sample |
The determination is carried out from a solution, |
||
|
product. It is allowed to determine the mass |
obtained in the determination of non-volatile |
||
|
howl fraction of heavy metals from the solution obtained in the determination of the mass fraction of non-volatile residue | |||
|
"Safety requirements" |
Missing |
||
|
"Manufacturer's warranty" |
Missing |
||
Acetic acid with the norms given in brackets was allowed to be produced until 01.01.95.
Editor V.N. Kopysov Technical editor V.N. Prusakova Proofreader M.I. Pershina Computer layout L.A. Circular
Handed over to the set 10/25/2006. Signed for publication on 08.11.2006. Format 60 x 84 Y 8 . Offset paper. Headset Times. Offset printing. Uel. oven l. 1.40. Uch.-ed. l. 1.25. Circulation 91 copies. Zach. 787. From 3345.
FSUE "Standartinform", 123995 Moscow, Granatny per., 4. Typed in FSUE "Standartinform" on a PC
Printed in the branch of FSUE "Standartinform" - type. "Moscow printer", 105062 Moscow, Lyalin per., 6
INTERSTATE STANDARD
REAGENTS
ACETIC ACID
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
By the Decree of the State Committee of Standards of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated March 24, 1975 No. 724, the introduction date was set
01.04.75
The validity period was removed according to protocol No. 5-94 of the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (IUS 11-12-94)
This standard applies to the reagent - acetic acid, which is a clear, colorless, flammable liquid with a pungent odor, miscible with water, ethyl alcohol in any ratio.
The technical level indicators established by this standard are provided for the highest quality category.
The standard contains all the requirements of the SEV 5375-85 standard.
The standard does not provide for requirements for a “clean” qualification product, the standards for a number of indicators have been tightened, sections have been included: “Safety requirements” and “Manufacturer's guarantees” (see the appendix on the compliance of the requirements of this standard with the requirements of the CMEA standard).
Formula CH 3 COOH.
Molecular weight (according to international atomic masses 1971) - 60.05.
1. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
1.1. Acetic acid must be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to the technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
1.2. According to physico-chemical parameters, acetic acid must comply with the requirements and standards given in Table. one.
Table 1
|
Name of indicator |
|||
|
Chemically pure ice (chemically pure ice) |
Chemically pure (chemically pure) |
Net for analysis (analytical grade) |
|
|
OKP 26 3411 048308 |
OKP 26 3411 047310 |
OKP 26 3411 047200 |
|
|
1. Appearance |
Clear colorless liquid |
||
|
2. Mass fraction of acetic acid (CH 3 COOH),%, not less than |
|||
|
3. Crystallization temperature, °C |
Not standardized |
||
|
4. Mass fraction of non-volatile residue,%, no more |
|||
|
5. Mass fraction of sulfates (SO 4),%, no more |
|||
|
6. Mass fraction of chlorides (Сl), %, no more |
|||
|
7. Mass fraction of iron (Fe),%, no more |
|||
|
8. Mass fraction of heavy metals (Pb),%, no more |
|||
|
9. Mass fraction of arsenic (As),%, no more |
|||
|
10. Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate in terms of oxygen (O),%, not more than |
|||
|
11. Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid (HCOOH),%, no more |
|||
|
12. Mass fraction of acetaldehyde (CH 3 CHO),%, no more |
|||
|
13. Mass fraction of acetic anhydride (CH 3 CO) 2 O,%, no more |
Not standardized |
||
|
14. Dilution test |
Must pass the test according to clause 3.14 |
||
Notes:
1. If the mass fraction of acetic anhydride does not exceed 0.001%, the words “without anhydride” are added to the qualification of the reagent.
2. Acetic acid with the norms given in brackets is allowed to be produced until 01.01.95.
Sec. one.
2a. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
2a. 1. Acetic acid belongs to the 3rd hazard class according to GOST 12.1.007-76.
The maximum permissible concentration of acetic acid vapors in the air of the working area (MAC) is 5 mg/m 3 .
Determination of vapors of acetic acid in the air is carried out by the iodometric method.
If the maximum permissible concentration is exceeded, a pair of acetic acid acts irritatingly on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract; acetic acid also causes skin burns.
2a.2. When working with acetic acid, you should use personal protective equipment (filtering gas masks of grades B and BKF), as well as observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Do not allow acetic acid to enter the body.
First aid for burns - abundant washing with water.
2a.3. Acetic acid is a flammable liquid with a pungent, specific odor.
Boiling point, °C .............................................. ................... 118.1
Flash point of vapors, °C .............................................. ........ 38
Ignition temperature, °C .............................................. ........ 68
Self-ignition temperature, °C .............................................. 454
Ignition area, volume fraction, %:
lower limit................................................ .............................. 3.3
upper limit................................................ ........................... 22
Temperature limits of ignition, °C:
lower limit................................................ ................................... 35
upper limit................................................ ....................... 76
Category and group of explosive mixture of acetic acid vapors with air PA-T1 (GOST 12.1.011-78*).
* GOST R 51330.2-99, GOST R 51330.5-99, GOST R 51330.11-99, GOST R 51330.19-99 are valid on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Work with acetic acid should be carried out away from fire. In case of fire, fire extinguishers should use PO-1D, PO-ZAI, Sampo foams, gas and powder compositions.
2a.4. Premises in which work with acetic acid is carried out must be equipped with general supply and exhaust mechanical ventilation.
The analysis of acetic acid should be carried out in a fume hood.
Sec. 2a. (Introduced additionally, Rev. No. 3).
2. ACCEPTANCE RULES
2.2. Determination of the content of sulfates, heavy metals, substances that reduce potassium permanganate, acetaldehyde and dilution tests is carried out by the manufacturer only at the request of the consumer and in the product intended for export.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3. METHODS OF ANALYSIS
3.1a. General instructions for the analysis - in accordance with GOST 27025-86.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 2).
rectified technical ethyl alcohol, the highest grade according to GOST 18300-87;
phenolphthalein (indicator) according to TU 6-09-5360-87, alcohol solution with a mass fraction of 1%, prepared according to GOST 4919.1-77;
equal-arm laboratory scales of the 2nd class model VLR-200 in accordance with GOST 24104-88 ** or any similar type with a division value of 0.0001 g.
3.2.2. Conducting an analysis
25 cm 3 of distilled water are placed in a conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 100 cm 3, weighed, 0.2 g of the product is added and the flask is weighed (the results of all weighings are recorded to the fourth decimal place), mixed thoroughly, titrated with sodium hydroxide solution in the presence of phenolphthalein until a persistent slightly pink color of the solution appears.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.2.3. Results processing
Mass fraction of acetic acid ( X) as a percentage is calculated by the formula
where m- weight of the sample of the product, g;
V- the volume of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 (0.1 N.) used for titration, cm 3;
0.006005 - the amount of acetic acid corresponding to 1 cm 3 of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 (0.1 n.), g.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.15% with a confidence level P = 0,95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.3a. Determination of the mass fraction of acetic acid by crystallization temperature
The determination is carried out according to clause 3.3 of this standard and according to GOST 18995.5-73.
The mass fraction of acetic acid in percent, depending on the crystallization temperature, is indicated in Table. 2.
table 2
|
Crystallization temperature, °С |
Crystallization temperature, °C |
Mass fraction of acetic acid, % |
|
In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of acetic acid, as well as in the analysis of the product of the qualification “x. h. ice”, the determination is carried out according to the crystallization temperature.
(Introduced additionally, Rev. No. 3).
3.3. Determination of crystallization temperature
The crystallization temperature of acetic acid is determined according to GOST 18995.5-73. In this case, preparation for analysis is carried out as follows: the device with the product is placed in a glass of water at a temperature of 5 °C - 7 °C. The product in the device is cooled to 10 ° C - 13 ° C and, without removing it from the glass, gently stir, without touching the bottom and walls of the test tube, until the first acid crystals appear.
At the moment of acid crystallization, the temperature rises sharply and, having reached a certain maximum, remains at this level for some time. For the crystallization temperature, noted with an error of 0.1 ° C, take the highest point of temperature rise.
3.4. Determination of the mass fraction of non-volatile residue
It is allowed to carry out the determination by the thiocyanate method from 20.0 cm 3 of a solution prepared according to clause 3.4, or by the 1,10-phenanthroline method without preliminary evaporation of 20.00 g of the sample of the analyzed product (corresponding to 19.0 cm 3).
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the mass of iron does not exceed:
for the drug, chemically pure ice and chemically pure - 0.004 mg,
for the drug pure for analysis - 0.02 mg.
In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of iron, the determination is carried out by the photocolorimetric 2.2"-dipyridyl method.
3.5 - 3.7. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.8. Determination of the mass fraction of heavy metals
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the observed color of the analyzed solution is not more intense than the color of the solution prepared simultaneously with the analyzed and containing in the same volume:
for chemically pure ice product - 0.01 mg Pb,
for chemically pure product - 0.01 mg Pb,
for product pure for analysis - 0.02 mg Pb
and the same amount of reagents.
It is allowed to carry out the determination from the corresponding volume of the solution prepared according to clause 3.4 after neutralizing it with an ammonia solution.
In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of heavy metals, the determination is carried out by the hydrogen sulfide method.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.9. Determination of the mass fraction of arsenic
In this case, preparation for the analysis is carried out as follows:
10.00 g (9.5 cm 3) of the analyzed product, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in the flask of the device for determining the arsenic content, 30 cm 3 of distilled water, 20 cm 3 of an acid solution, 1 cm 3 of a solution of tin dichloride are added , mixed and then the determination is carried out according to GOST 10485-75.
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the observed color of the bromine-mercury paper of the analyzed solution is not more intense than the color of the bromine-mercury paper of the solution prepared simultaneously with the analyzed and containing in the same volume:
for chemically pure ice product - 0.0015 mg As,
for a chemically pure product - 0.005 mg As,
for a product pure for analysis - 0.005 mg As
and the same amount of reagents.
3.10. Determination of the mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate in terms of oxygen (O)
3.10.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.10.2. Conducting an analysis
10.00 g (9.5 cm 3) of the analyzed product, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in a conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 500 cm 3, 10 cm 3 of sulfuric acid are added, the solution is cooled to 18 ° C - 20 ° C, add 1 cm 3 of potassium dichromate solution and mix.
Simultaneously prepare a control solution under the same conditions, with the same amounts of reagents and solutions.
The analyzed and control solutions are left for 30 minutes. Then, 50 cm 3 of distilled water are added to both solutions, mixed, cooled to 18 ° C - 20 ° C, 10 cm 3 of potassium iodide solution are added, closed with a cork, mixed and left in a dark place for 10 minutes. The cork, neck and walls of the flask are washed off with 150 cm 3 of distilled water and the released iodine is titrated from a microburette with a solution of sodium sulphate in the presence of starch until the solution becomes colorless.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.10.3. Results processing
The mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate, in terms of oxygen ( X 2), as a percentage is calculated by the formula
where m- weight of the sample of the product, g;
V- the volume of a solution of sodium sulphate with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 used for titration of the control solution, cm 3;
V 1 - the volume of a solution of sodium sulphate with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 used for titration of the analyzed product, cm 3;
0.0008 - the amount of oxygen corresponding to 1 cm 3 of a solution of potassium dichromate with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3, g.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.001% with a confidence level P = 0,95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.11. Determination of the mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid
3.11.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.11.2. Conducting an analysis
10 g (9.5 cm 3 ) of the product to be analyzed, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in a 250 cm 3 conical flask with a ground stopper containing 70 cm 3 of water. 15 cm 3 of a sulfuric acid solution, 50 cm 3 of a potassium permanganate solution are added to the solution and heated in a thermostat at 80 ° C for 15 minutes. The flask is cooled for 10 minutes with running water, 2 g of potassium iodide are added and left alone for 5 minutes. The released iodine is titrated with a solution of sodium sulphate, and 2 cm 3 of a starch solution are added at the end of the titration.
At the same time, a control solution is prepared under the same conditions with the same amounts of reagents and solutions as in the analyzed solution.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.11.3. Results processing
Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid ( X 3), as a percentage, is calculated by the formula
where m- weight of the sample of the product, g;
V 1 - the volume of a solution of sodium sulphate with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol / dm 3 used for titration in the control solution, cm 3;
V- the volume of sodium sulphate solution with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol/dm 3 used for titration of the analyzed product, cm 3 ;
0.00023 - the amount of formic acid corresponding to 1 cm 3 of a solution of potassium permanganate with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol / dm 3, g.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.0005% with a confidence level P = 0,95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.12. Determination of the mass fraction of acetaldehyde (CH 3 CHO)
nozzle H 1 29/32-14/23-14/23 or bend I< 750 ° 2К 29/32-14/23 по ГОСТ 25336-82 ;
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the mass of acetaldehyde does not exceed:
for chemically pure ice product - 0.2 mg,
for chemically pure product - 0.4 mg,
for a product pure for analysis - 0.6 mg.
(Changed edition, Rev. No. 2, 3).
3.13. Determination of the mass fraction of acetic anhydride
3.13.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
pipettes 2-2-25 (or 2-2-50 or 2-2-5), 2-2-10 according to GOST 29169-91.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.13.2. Conducting an analysis
25 cm 3 of the product are placed in a dry conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 100 cm 3 , 10 cm 3 of an aniline solution are added, closed with a stopper, mixed and incubated for 10 minutes. Then add one drop of crystal violet solution and titrate with perchloric acid until the color changes to green. Simultaneously prepare a control solution under the same conditions, with the same amounts of reagents and solutions.
If, during back titration, a change in the color of the analyzed solution occurs from a few drops of perchloric acid solution, which indicates that the mass fraction of acetic anhydride in the analyzed product is more than 0.03%, then an additional amount of aniline should be added to the control solution and the exposure should be allowed again for 10 minutes.
If the mass fraction of acetic anhydride in the analyzed product is less than 0.005%, 50 cm 3 of the product are taken for determination, if the mass fraction is more than 0.05%, 5 cm 3 or 10 cm 3 of the product are taken.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.13.3. Results processing
Mass fraction of acetic anhydride ( X 4) as a percentage calculated by the formula
where V- the volume of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 used for titration in the control solution, cm 3;
V 1 - the volume of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 used for titration of the analyzed product, cm 3;
0.0102 - the amount of acetic anhydride corresponding to 1 cm 3 of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3, g;
1.0498 - density of acetic acid, g/cm 3 .
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.002% with a confidence level P= 0,95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.14. dilution test
10 cm 3 of the product is diluted with 30 cm 3 of distilled water (GOST 6709-72) and mixed.
The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the solution remains clear for 1 h.
4. PACKAGING, LABELING, TRANSPORT AND STORAGE
4.1. Packaging and labeling - in accordance with GOST 3885-73.
Type and type of container: 3-1, 3-2, 3-5, 3-8, 8-1, 8-2, 8-5, 9-1, 10-1.
Packing group: V, VI, VII.
For packing containers with acetic acid, wood shavings impregnated with solutions of calcium chloride, magnesium chloride or ammonium sulphate, as well as slag wool or other non-combustible sealing material, are used.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
4.2. A danger sign is applied to the container according to GOST 19433-88 (class 8, subclass 8.1, drawing 8 - main, drawing 3 - additional, classification code 8142, UN serial number 2789).
4.3. The product is transported by all modes of transport in accordance with the rules for the transport of flammable goods.
4.4. The product is stored in closed containers in rooms specially adapted for the storage of flammable substances, protected from direct sunlight and precipitation.
5. MANUFACTURER WARRANTY
5.1. The manufacturer guarantees the compliance of acetic acid with the requirements of this standard, subject to the conditions of transportation and storage.
5.2. Guaranteed shelf life of the product is one year from the date of manufacture.
Sec. five. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
Sec. 6. (Deleted, Rev. No. 3).
APPENDIX
Mandatory
Compliance with the requirements of GOST 61-75 ST SEV 5375-85
|
ST SEV 5375-85 |
|||
|
There are no standards for qualifying pure |
Established standards for qualifying clean |
||
|
Mass fraction of acetic acid, %, not less than for qualifications: |
|||
|
X. h. ice 99.8 |
X. h. ice 99.8 (99.5) |
||
|
X. hours 99.5 (99.0) |
|||
|
h.d.a. 99.5 |
h.d.a. 99 (98) |
||
|
Mass fraction of sulfates, %, not more than for qualification |
|||
|
X. h. ice 0.0001 |
X. h. ice 0.0002 |
||
|
Mass fraction of iron, %, no more than for qualifications: |
|||
|
X. h. ice 0.00002 |
X. h. ice 0.00002 (0.00005) |
||
|
X. hours 0.00002 (0.00005) |
|||
|
Mass fraction of heavy metals, %, not more than for qualifications: |
|||
|
X. h. ice 0.00003 |
X. h. ice 0.00005 |
||
|
X. hours 0.00005 (0.00008) |
|||
|
Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate,%, not more than for qualification |
|||
|
X. h. ice 0.003 |
X. h. ice 0.003 (0.005) |
||
|
The determination is carried out from a sample of the product. It is allowed to determine the mass fraction of heavy metals from the solution obtained when determining the mass fraction of non-volatile residue |
The determination is carried out from the solution obtained in the determination of non-volatile residue |
||
|
"Safety requirements" |
Missing |
||
|
"Manufacturer's warranty" |
Missing |
||
GOST 61-75
INTERSTATE STANDARD
REAGENTS
ACETIC ACID
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
By the Decree of the State Committee of Standards of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated March 24, 1975 No. 724, the introduction date was set
01.04.75
The validity period was removed according to protocol No. 5-94 of the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (IUS 11-12-94)
This standard applies to the reagent - acetic acid, which is a clear, colorless, flammable liquid with a pungent odor, miscible with water, ethyl alcohol in any ratio.
The technical level indicators established by this standard are provided for the highest quality category.
The standard contains all the requirements of the SEV 5375-85 standard.
The standard does not provide for requirements for a “clean” qualification product, the standards for a number of indicators have been tightened, sections have been included: “Safety requirements” and “Manufacturer's guarantees” (see the appendix on the compliance of the requirements of this standard with the requirements of the CMEA standard).
Formula CH 3 COOH.
Molecular weight (according to international atomic masses 1971) - 60.05.
1. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
1.1. Acetic acid must be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to the technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
1.2. According to physico-chemical parameters, acetic acid must comply with the requirements and standards given in Table. .
Table 1
|
Chemically pure ice (chemically pure ice) |
Chemically pure (chemically pure) |
Net for analysis (analytical grade) |
|
|
OKP 26 3411 048308 |
OKP 26 3411 047310 |
OKP 26 3411 047200 |
|
|
1. Appearance |
Clear colorless liquid |
||
|
2. Mass fraction of acetic acid (CH 3 COOH),%, not less than |
|||
|
3. Crystallization temperature, °C |
Not standardized |
||
|
4. Mass fraction of non-volatile residue,%, no more |
|||
|
5. Mass fraction of sulfates (SO 4),%, no more |
|||
|
6. Mass fraction of chlorides (Сl), %, no more |
|||
|
7. Mass fraction of iron (Fe),%, no more |
|||
|
8. Mass fraction of heavy metals (Pb),%, no more |
|||
|
9. Mass fraction of arsenic (As),%, no more |
|||
|
10. Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate in terms of oxygen (O),%, not more than |
|||
|
11. Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid (HCOOH),%, no more |
|||
|
12. Mass fraction of acetaldehyde (CH 3 CHO),%, no more |
|||
|
13. Mass fraction of acetic anhydride (CH 3 CO) 2 O,%, no more |
Not standardized |
||
|
14. Dilution test |
Must pass the test of |
||
Notes:
1. If the mass fraction of acetic anhydride does not exceed 0.001%, the words “without anhydride” are added to the qualification of the reagent.
2. Acetic acid with the norms given in brackets is allowed to be produced until 01.01.95.
The maximum permissible concentration of acetic acid vapors in the air of the working area (MAC) is 5 mg/m 3 .
Determination of vapors of acetic acid in the air is carried out by the iodometric method.
If the maximum permissible concentration is exceeded, a pair of acetic acid acts irritatingly on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract; acetic acid also causes skin burns.
2a.2. When working with acetic acid, you should use personal protective equipment (filtering gas masks of grades B and BKF), as well as observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Do not allow acetic acid to enter the body.
First aid for burns - abundant washing with water.
2a.3. Acetic acid is a flammable liquid with a pungent, specific odor.
Boiling point, °C .............................................. ................... 118.1
Flash point of vapors, °C .............................................. ........ 38
Ignition temperature, °C .............................................. ........ 68
Self-ignition temperature, °C .............................................. 454
Ignition area, volume fraction, %:
lower limit................................................ .............................. 3.3
upper limit................................................ ........................... 22
Temperature limits of ignition, °C:
lower limit................................................ ................................... 35
upper limit................................................ ....................... 76
Category and group of explosive mixture of acetic acid vapors with air PA-T1 (GOST 12.1.011-78*).
___________
* GOST R 51330.2-99, GOST R 51330.5-99, GOST R 51330.11-99, GOST R 51330.19-99 are valid on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Work with acetic acid should be carried out away from fire. In case of fire, fire extinguishers should use PO-1D, PO-ZAI, Sampo foams, gas and powder compositions.
2a.4. Premises in which work with acetic acid is carried out must be equipped with general supply and exhaust mechanical ventilation.
The analysis of acetic acid should be carried out in a fume hood.
2.2. Determination of the content of sulfates, heavy metals, substances that reduce potassium permanganate, acetaldehyde and dilution tests is carried out by the manufacturer only at the request of the consumer and in the product intended for export.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3. METHODS OF ANALYSIS
3.1a. General instructions for the analysis - in accordance with GOST 27025-86.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 2).
3.1. Samples are taken according to GOST 3885-73. The mass of the average sample must be at least 2 kg (1.9 dm 3).
3.2a. Appearance definition
Appearance is determined at 20 ° C visually by comparison with distilled water according to GOST 14871-76. In this case, the analyzed product should not have opalescence and should not contain mechanical particles.
(Introduced additionally, Rev. No. 3).
3.2. Determination of the mass fraction of acetic acid by alkalimetric titration
3.2.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware
Distilled water, not containing carbon dioxide; prepared according to GOST 4517-87;
sodium hydroxide according to GOST 4328-77, concentration solution from(NaOH) \u003d 0.1 mol / dm 3 (0.1 N), prepared according to GOST 25794.1-83;
rectified technical ethyl alcohol, the highest grade according to GOST 18300-87;
phenolphthalein (indicator) according to TU 6-09-5360-87, alcohol solution with a mass fraction of 1%, prepared according to GOST 4919.1-77;
equal-arm laboratory scales of the 2nd class model VLR-200 in accordance with GOST 24104-88 ** or any similar type with a division value of 0.0001 g.
___________
3.2.2. Conducting an analysis
25 cm 3 of distilled water are placed in a conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 100 cm 3, weighed, 0.2 g of the product is added and the flask is weighed (the results of all weighings are recorded to the fourth decimal place), mixed thoroughly, titrated with sodium hydroxide solution in the presence of phenolphthalein until a persistent slightly pink color of the solution appears.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
3.2.3. Results processing
Mass fraction of acetic acid (X) as a percentage is calculated by the formula
![]()
where m- weight of the sample of the product, g;
V- the volume of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 (0.1 N.) used for titration, cm 3;
0.006005 - the amount of acetic acid corresponding to 1 cm 3 of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 (0.1 n.), g.
The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.15% with a confidence levelP = 0,95.
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 3).
The determination is carried out according to clause of this standard and according to GOST 18995.5-73.
The mass fraction of acetic acid in percent, depending on the crystallization temperature, is indicated in Table. .
table 2
|
It is allowed to carry out the determination by the thiocyanate method from 20.0 cm 3 of a solution prepared according to p. The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the mass of iron does not exceed: for the drug, chemically pure ice and chemically pure - 0.004 mg, for the drug pure for analysis - 0.02 mg. In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of iron, the determination is carried out by the photocolorimetric 2.2"-dipyridyl method. 3.5 - 3.7. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the observed color of the analyzed solution is not more intense than the color of the solution prepared simultaneously with the analyzed and containing in the same volume: for chemically pure ice product - 0.01 mg Pb, for chemically pure product - 0.01 mg Pb, for product pure for analysis - 0.02 mg Pb It is allowed to carry out the determination from the corresponding volume of the solution prepared according to paragraph after neutralizing it with an ammonia solution. In case of disagreement in the assessment of the mass fraction of heavy metals, the determination is carried out by the hydrogen sulfide method. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). 3.9. Determination of the mass fraction of arsenic The determination is carried out according to GOST 10485-75. In this case, preparation for the analysis is carried out as follows: 10.00 g (9.5 cm 3) of the analyzed product, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in the flask of the device for determining the arsenic content, 30 cm 3 of distilled water, 20 cm 3 of an acid solution, 1 cm 3 of a solution of tin dichloride are added , mixed and then the determination is carried out according to GOST 10485-75. The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the observed color of the bromine-mercury paper of the analyzed solution is not more intense than the color of the bromine-mercury paper of the solution prepared simultaneously with the analyzed and containing in the same volume: for chemically pure ice product - 0.0015 mg As, for a chemically pure product - 0.005 mg As, for a product pure for analysis - 0.005 mg As and the same amount of reagents. 3.10. Determination of the mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate in terms of oxygen (O) 3.10.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware Distilled water according to GOST 6709-72 potassium dichromate according to GOST 4220-75, concentration solution from(1/6 K 2Cr2 About 7) \u003d 0.1 mol / dm 3 (0.1 N), prepared according to GOST 25794.2-83; (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). 3.10.2. Conducting an analysis 10.00 g (9.5 cm 3) of the analyzed product, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in a conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 500 cm 3, 10 cm 3 of sulfuric acid are added, the solution is cooled to 18 ° C - 20 ° C, add 1 cm 3 of potassium dichromate solution and mix. Simultaneously prepare a control solution under the same conditions, with the same amounts of reagents and solutions. The analyzed and control solutions are left for 30 minutes. Then, 50 cm 3 of distilled water are added to both solutions, mixed, cooled to 18 ° C - 20 ° C, 10 cm 3 of potassium iodide solution are added, closed with a cork, mixed and left in a dark place for 10 minutes. The cork, neck and walls of the flask are washed off with 150 cm 3 of distilled water and the released iodine is titrated from a microburette with a solution of sodium sulphate in the presence of starch until the solution becomes colorless. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). 3.10.3. Results processing The mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium dichromate, in terms of oxygen ( X 2), as a percentage is calculated by the formula
where m- weight of the sample of the product, g; V- the volume of a solution of sodium sulphate with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 used for titration of the control solution, cm 3; V 1 - the volume of a solution of sodium sulphate with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol/dm 3 used for titration of the analyzed product, cm 3 ; 0.0008 - the amount of oxygen corresponding to 1 cm 3 of a solution of potassium dichromate with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3, g. The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.001% with a confidence levelP = 0,95. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). 3.11. Determination of the mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid 3.11.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware Distilled water according to GOST 6709-72, distilled in the presence of potassium permanganate; potassium permanganate according to GOST 20490-75, concentration solution from(1/5KMnO 4 ) \u003d 0.01 mol / dm 3 (0.01 N.), freshly prepared, prepared according to GOST 25794.2-83; pipettes 6-2-10, 2-2-50, 4-2-2 according to GOST 29169-91; (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). 3.11.2. Conducting an analysis 10 g (9.5 cm 3 ) of the analyzed product, measured to the first decimal place, are placed in a 250 cm 3 conical flask with a ground stopper containing 70 cm 3 of water. 15 cm 3 of a sulfuric acid solution, 50 cm 3 of a potassium permanganate solution are added to the solution and heated in a thermostat at 80 ° C for 15 minutes. The flask is cooled for 10 minutes with running water, 2 g of potassium iodide are added and left alone for 5 minutes. The released iodine is titrated with a solution of sodium sulphate, and 2 cm 3 of a starch solution are added at the end of the titration. At the same time, a control solution is prepared under the same conditions with the same amounts of reagents and solutions as in the analyzed solution. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). 3.11.3. Results processing Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate in terms of formic acid (X 3 ), as a percentage, is calculated by the formula
where m- weight of the sample of the product, g; V 1 - the volume of a solution of sodium sulphate with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol / dm 3 used for titration in the control solution, cm 3; V- the volume of sodium sulphate solution with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol/dm 3 used for titration of the analyzed product, cm 3 ; 0.00023 - the amount of formic acid corresponding to 1 cm 3 of a solution of potassium permanganate with a concentration of exactly 0.01 mol / dm 3, g. The result of the analysis is taken as the arithmetic mean of two parallel determinations, the allowable discrepancies between which should not exceed 0.0005% with a confidence levelP = 0,95. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). 3.12. Determination of the mass fraction of acetaldehyde (CH 3 CHO) The determination is carried out according to GOST 16457-76 by photometric or visual-colorimetric method. At the same time, a device for the determination of acetaldehyde is assembled (see drawing), consisting of: flasks OG-2-500-29/32 or KGU-2-1-500-29/32 according to GOST 25336-82; nozzle H 1 29/32-14/23-14/23 or bend I< 750 ° 2К 29/32-14/23 по ГОСТ 25336-82 ; refrigerator KhPT 1-100-14/23 according to GOST 25336-82; along AIO-14 / 23-14 / 23-60 according to GOST 25336-82, elongated with a glass tube; 20.00 g (19.0 cm 3) of the analyzed product, measured with a pipette with a capacity of 25 cm 3 (GOST 29169-91) with an accuracy of the first decimal place, is placed in the dropping funnel of the device. Device for the determination of acetaldehyde (scheme)
1 - distillation flask; 2 - capillaries or pumice; 3 - drip funnel; 4 - receiver Several glass capillaries fused at one end are introduced into the flask of a distillation device with a capacity of 500 cm 3, and about 40 cm 3 of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass fraction of 30% (GOST 4328-77) is poured. The number of milliliters of sodium hydroxide required to neutralize 20 g of the product is preliminarily determined in a separate experiment by appropriate titration in the presence of universal indicator paper to pH 7. The flask with the contents is closed with a stopper, through which the end of the refrigerator tube with a spray trap and the end of the dropping funnel are passed. The other end of the refrigerator tube should be slightly immersed in water (5 cm 3) contained in a cylinder marked with 5 and 15 cm 3. From the dropping funnel, the product is poured into the flask, then 2–3 drops of an alcohol solution of phenolphthalein with a mass fraction of 0.1%, prepared according to GOST 4919.1-77, are introduced into the flask of the device through the funnel. If necessary, neutralize the contents of the flask with the product or sodium hydroxide solution, adding it dropwise to a faint pink color. The tap of the dropping funnel is closed and when heated, 10 cm 3 of liquid is distilled into the receiver, closing it with a ground stopper, mixed, the volume of the solution is adjusted with water to 23 cm 3 and then the determination is carried out according to GOST 16457-76. The product is considered to comply with the requirements of this standard if the mass of acetaldehyde does not exceed: for chemically pure ice product - 0.2 mg, for chemically pure product - 0.4 mg, for a product pure for analysis - 0.6 mg. (Changed edition, Rev. No. 2, 3). 3.13. Determination of the mass fraction of acetic anhydride 3.13.1. Reagents, solutions and glassware pipettes 2-2-25 (or 2-2-50 or 2-2-5), 2-2-10 according to GOST 29169-91. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). 3.13.2. Conducting an analysis 25 cm 3 of the product are placed in a dry conical flask with a ground stopper with a capacity of 100 cm 3 , 10 cm 3 of an aniline solution are added, closed with a stopper, mixed and incubated for 10 minutes. Then add one drop of crystal violet solution and titrate with perchloric acid until the color changes to green. Simultaneously prepare a control solution under the same conditions, with the same amounts of reagents and solutions. If, during back titration, a change in the color of the analyzed solution occurs from a few drops of perchloric acid solution, which indicates that the mass fraction of acetic anhydride in the analyzed product is more than 0.03%, then an additional amount of aniline should be added to the control solution and the exposure should be allowed again for 10 minutes. If the mass fraction of acetic anhydride in the analyzed product is less than 0.005%, 50 cm 3 of the product are taken for determination, if the mass fraction is more than 0.05%, 5 cm 3 or 10 cm 3 of the product are taken. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). 3.13.3. Results processing Mass fraction of acetic anhydride (X 4 ) as a percentage is calculated by the formula
where V- the volume of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3 used for titration in the control solution, cm 3; V 1 - the volume of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol/dm 3 used for titration of the analyzed product, cm 3 ; 0.0102 - the amount of acetic anhydride corresponding to 1 cm 3 of an acetic acid solution of perchloric acid with a concentration of exactly 0.1 mol / dm 3, g;. Type and type of container: 3-1, 3-2, 3-5, 3-8, 8-1, 8-2, 8-5, 9-1, 10-1. Packing group: V, VI, VII. For packing containers with acetic acid, wood shavings impregnated with solutions of calcium chloride, magnesium chloride or ammonium sulphate, as well as slag wool or other non-combustible sealing material, are used. (Revised edition, Rev. No. 3). 4.2. A danger sign is applied to the container according to GOST 19433-88 (class 8, subclass 8.1, drawing 8 - main, drawing 3 - additional, classification code 8142, UN serial number 2789). 4.3. The product is transported by all modes of transport in accordance with the rules for the transport of flammable goods. 4.4. The product is stored in closed containers in rooms specially adapted for the storage of flammable substances, protected from direct sunlight and precipitation. |
|||
|
There are no standards for qualifying pure |
Established standards for qualifying clean |
||
|
Mass fraction of acetic acid, %, not less than for qualifications: |
|||
|
X. h. ice 99.8 |
X. h. ice 99.8 (99.5) |
||
|
X. hours 99.5 (99.0) |
|||
|
h.d.a. 99.5 |
h.d.a. 99 (98) |
||
|
Mass fraction of sulfates, %, not more than for qualification |
|||
|
X. h. ice 0.0001 |
X. h. ice 0.0002 |
||
|
Mass fraction of iron, %, no more than for qualifications: |
|||
|
X. h. ice 0.00002 |
X. h. ice 0.00002 (0.00005) |
||
|
X. hours 0.00002 (0.00005) |
|||
|
Mass fraction of heavy metals, %, not more than for qualifications: |
|||
|
X. h. ice 0.00003 |
X. h. ice 0.00005 |
||
|
X. hours 0.00005 (0.00008) |
|||
|
Mass fraction of substances that reduce potassium permanganate,%, not more than for qualification |
|||
|
X. h. ice 0.003 |
X. h. ice 0.003 (0.005) |
||
|
The determination is carried out from a sample of the product. It is allowed to determine the mass fraction of heavy metals from the solution obtained when determining the mass fraction of non-volatile residue |
The determination is carried out from the solution obtained in the determination of non-volatile residue |
||
|
"Safety requirements" |
Missing |
||
|
"Manufacturer's warranty" |
Popular |